The Ampcamper: An RV Adventure
I’m about to depart for three weeks towing a 30-year-old RV trailer with an electric vehicle up and down the Rocky Mountains and into various national parks, off grid. With me will be my teenage daughter and niece and a fairly large dog. Surely something will go wrong.

I had been digitizing old family media for a few years after my father passed away when I stumbled upon a unique photo — actually a 35mm slide because projected slides were social media in the late 70’s. It depicted a map and had clearly been drawn on. After a little sleuthing I determined it was the route my family took in a motorhome we owned for a few years on a three-week trip which came to be known thereafter as “the three-week trip”.
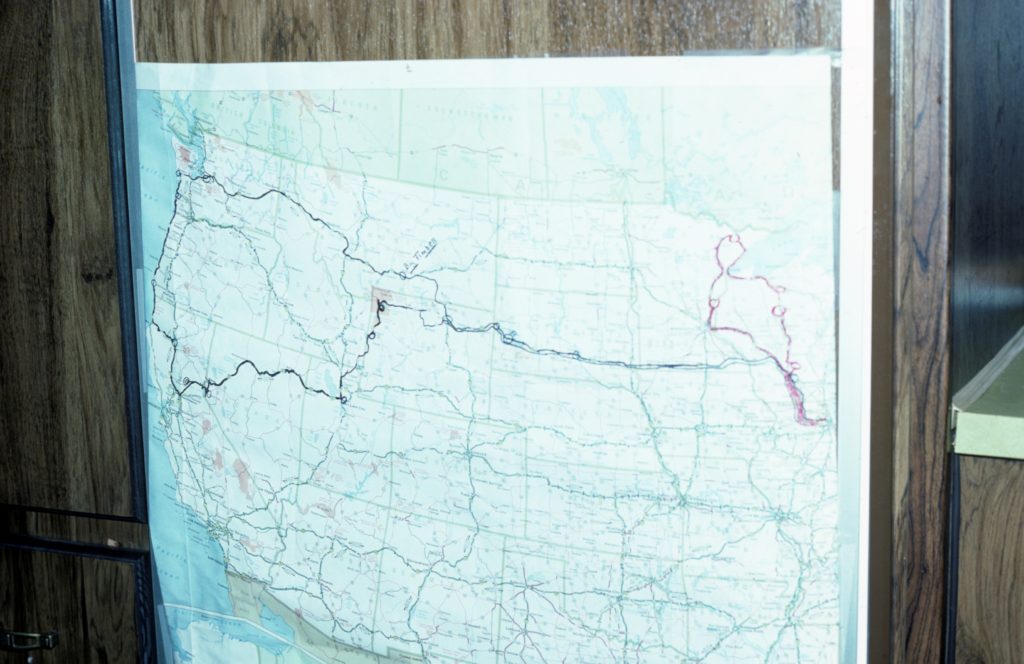
My father loved that motorhome. I think it was as close as he could get to his fantasy of being a cross-country big rig truck driver, role-playing Convoy. I recall very little of the sites or destinations we visited in that thing, but I do remember being inside what seemed a massive vehicle to young me. So on finding the map I knew I had to recreate at least a part of the journey at some point. Well, that point is now.
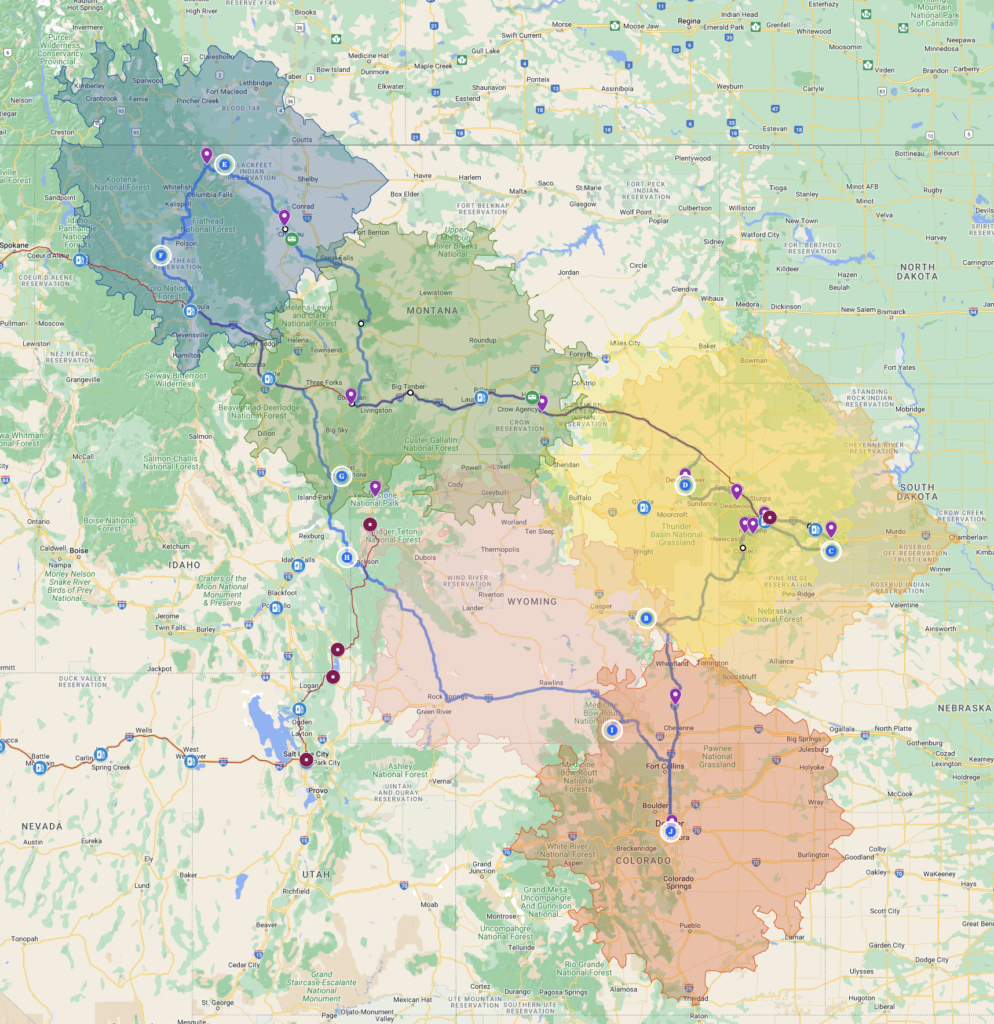
Starting point: Denver. My father’s original route is the thin red line above and we pretty quickly determined that actually recreating the trip (which swung all the way out to the Pacific Northwest and down the west coast) would take up most of the summer. How ol’ dad pulled this off in three weeks — including transiting the northern plans to/from Chicago — I have no idea.
So our upcoming route basically breaks down into thirds: Black Hills/Badlands, Glacier National Park, and Yellowstone. We pick up my dad’s route along I-90 west and then again at Yellowstone. Glacier itself is a bit of a detour (which I want to see for obvious reasons), so we’re not being overly faithful to the original, though we are trying to at least stop at some of the places he’s circled on the map. Why, for instance, Big Timber, Montana? No clue. But we’re gonna find out — or at least make up a reason we think he circled it.
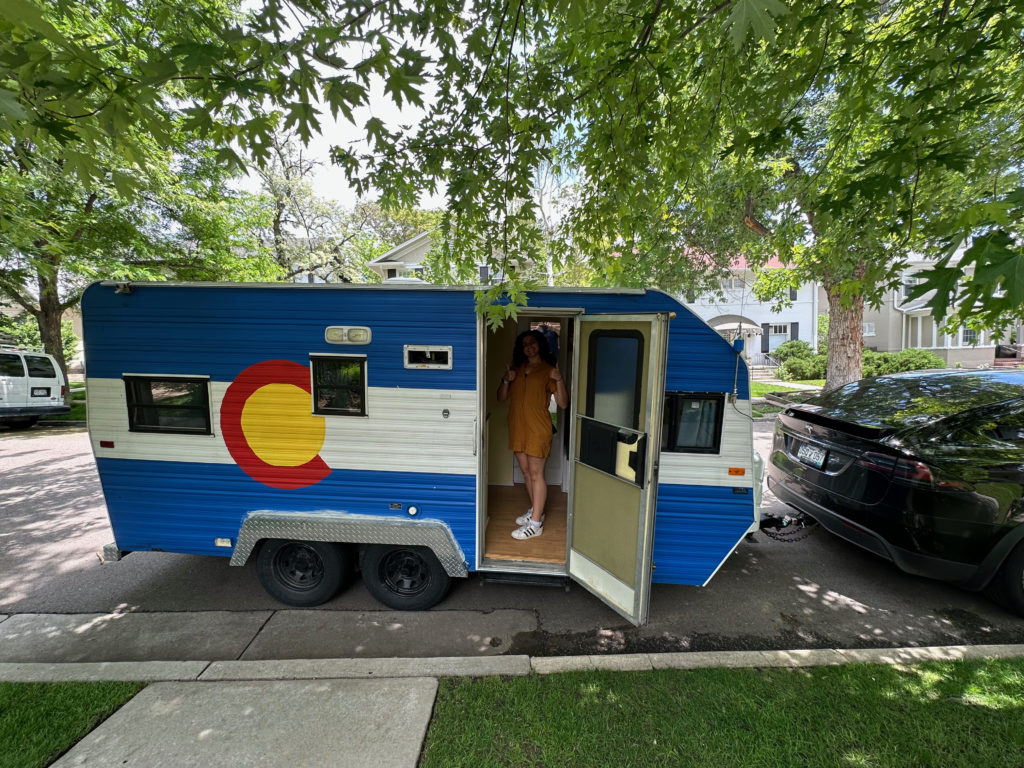

The second challenge was finding a vehicle. RV envy is real, especially when you have friends who’ve done it just right. I considered renting a big motorhome to recreate my childhood experience, but maybe (I wondered) the reason I have no recollection of actually seeing sights from those trips is because we couldn’t actually park that beast anywhere desirable? With some previous experience visiting national parks and kooky Americana I knew that vehicle flexibility was key. So we settled on a trailer-towing arrangement so that we can unhitch and tool around as needed. But what to tow?
It’s good to have outdoorsy friends, especially close friends you’ve known since rooming together in college. And this is how I have come into the temporary possession of the glorious Colorado flag-themed (handpainted!) 1993 Sunline camper trailer above. There are no bells and whistles on this thing whatsoever and it is kinda falling apart, but it works and tows like a dream. Much more on our home-away-from-home in posts as we hit the road.
OK so, how to tow? I have been driving an electric vehicle for several years and have come to love the national Tesla charging network (though not so much the company’s leader). So why not make this odyssey needlessly (more) complex and attempt to haul a two-ton trailer on electrons alone? I did a few test runs and the range impact is basically exactly what you’d expect from an internal combustion engine: 43.3 % average reduction in range, 55.6 % average reduction in efficiency. Conservatively that means 175 miles of range per full charge. The colored polygons on the map above show roughly how far we can go from major destinations on a charge. (The tribulations of charging with a trailer, especially in the EV infrastructure wasteland of Wyoming and Montana, will get its own post.)
I’ll post as regularly as I can once we depart with some special features including what it is like to outfit this quasi-futurist jalopy with a CB radio. Everything will be cataloged at http://ampcamper.com with updates at Instagram and Bluesky.
If anyone reading this lives around the route or has recommendations what to see, hit us up!
Here’s a full map and itinerary spreadsheet.
10 days and counting …
Ghost Ecosystems
I teach a course at CU Denver on urban technologies where, to the bewilderment of most students, we begin by studying a decrepit urban typology somewhat unique to the American West: ghost towns. Where students are expecting robot cars and sparkling sci-fi skylines they get depopulated ruins and crumbling foundations. It takes several sessions before students appreciate why we start this way. The afterlife of towns and cities exposes quite a bit about why they were created, what assumptions they were built upon, and what larger systems they are enmeshed in. If these towns are ghosts, how exactly did they die?

Apart from their educational value, ghost towns in the western US are uniquely fun to explore, little open-air museums of urban decay which defy assimilation into newer development as happens in the east. And it’s not just towns: ghost infrastructure is everywhere, like the time-smoothed scar tissue of historic Route 66 reminding how we stitched together the country west of Chicago in the early 20th century.
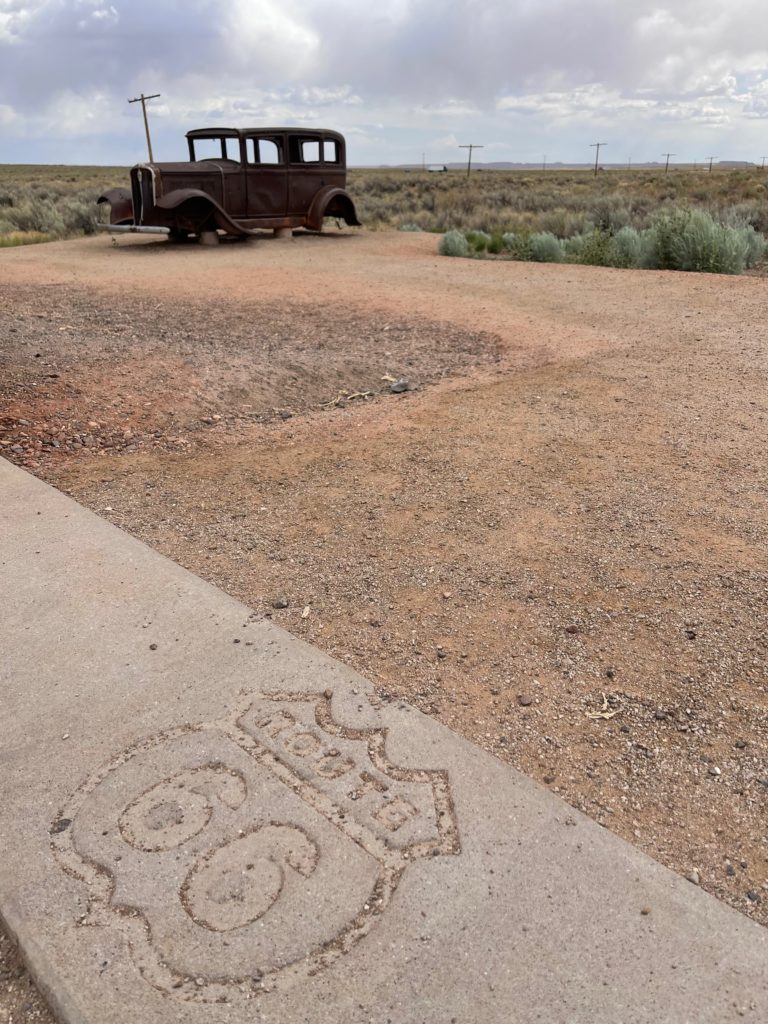

More personally, as a relative newcomer to Colorado from the midwest I’ve come to love ghost towns simply for the excuse they provide to explore the region I now call home. Placemaking by way of un-places.
So it seems somewhat obvious in hindsight that I’d inevitably be drawn to dinosaurs, an even more complex and further bygone ecosystem whose presence in the American West is as iconic as tumbleweeds and spurs. Dinosaurs may seem like quite a conceptual leap from ghost towns. But both are sometimes barely visible threads woven into the fabric of our landscapes here, simultaneously a record of engagement with, modification of, and sometimes defeat by the environment itself. This interplay between environment and the creatures that lived in it — indeed were ultimately ended by it — I think accounts for its hold on me, someone with zero paleontology or geology (and very little biology) background. How could an ecosystem as complex as that of the Age of Reptiles, lasting hundreds of millions of years through several extinction events, simply end? Indeed, did it really end? (Hello, birds!) Like ghost towns, the dinosaurs that once prowled (and flew and swam) here have been remade into a kind of modern brand. From gas station logos to baseball team mascots to entire town identities these “terrible lizards” seem endlessly repurposeable.
My first descent into this mild mania actually began not in Colorado but where it all ended off the coast of the Yucatán peninsula.
Vacationing there last year naturally I had to educate myself on the cataclysm of the bolide impact 66 million years ago which brought an end to (almost) all dinosaurs. Once I felt I knew enough I then put together a small lecture, to the chagrin of my family and friends who just wanted beachside rest and relaxation. But that impact! Obviously everything in our locale was obliterated, instantly pulverized, but it was the thought of what the world became in the years and decades after the fiery hellstorm that really got me thinking. A world choked by carbon and airborne particulates, sunless, scorched from heat coming in from the sun but having no way to radiate back out.
How a geologist named Walter Alvarez enlisted his physicist father Luis to figure out just why the boundary in rock sediment separating the Cretaceous period (lots of dinosaur fossils) from the Paleogene period (nary a dinosaur fossil) has levels of the element Iridium 100 times higher than naturally occuring is a story worth reading. Ultimately this layer, called the K-T or K-Pg boundary, and which can be found nearly everywhere on our planet, is the blanket of asteroid material that fell back to Earth after its immolation off the Yucatán — a burial shroud placed gently (and permanently) in the geologic record eulogizing almost 75% of all species at the time.

This was all good fun … until I decided to make a solo mountain bike day trip to Picket Wire Canyonlands in southwest Colorado last year. The trek about killed me — hot, dry, arduous biking on sandy trails. Also I didn’t bring enough water. On the other hand, I had the entire 16.7 trail route to myself, seeing not another soul the whole day. This solitary experience became all the more magical when I arrived at my destination, the largest dinosaur tracksite in North America. 150 million years ago plant-chomping Apatosaurus and flesh-ripping Allosaurus squished their feet into the soft lakeshore here which silted over and hardened into over 1,300 tracks in at least 100 separate paths criss-crossing every which way. I dismounted my bike right in the middle of it all, sat on the sun-baked rock, reveled in a total lack of cell signal, and tried to imagine what the place would have looked like — sounded like, smelled like! — as the herds slopped through.

And then I was hooked. How could I not learn more at this point? I had placed my foot inside the footprint of another living creature from the Jurassic period out on a bike ride just a few hours from my home.
Sure, Sue the T-Rex was found in South Dakota. Montana has the infamous Hell Creek Formation. Utah gave us the raptor that successfully retconned Spielberg’s originally ludicrous depiction of Velociraptors in Jurassic Park. Even Kansas can flaunt its one-time Western Interior Seaway and basically all the great marine reptile and pterosaur specimens.
But Colorado is the state that I think most fulsomely embraces its dinosaur history. Here are some highlights.
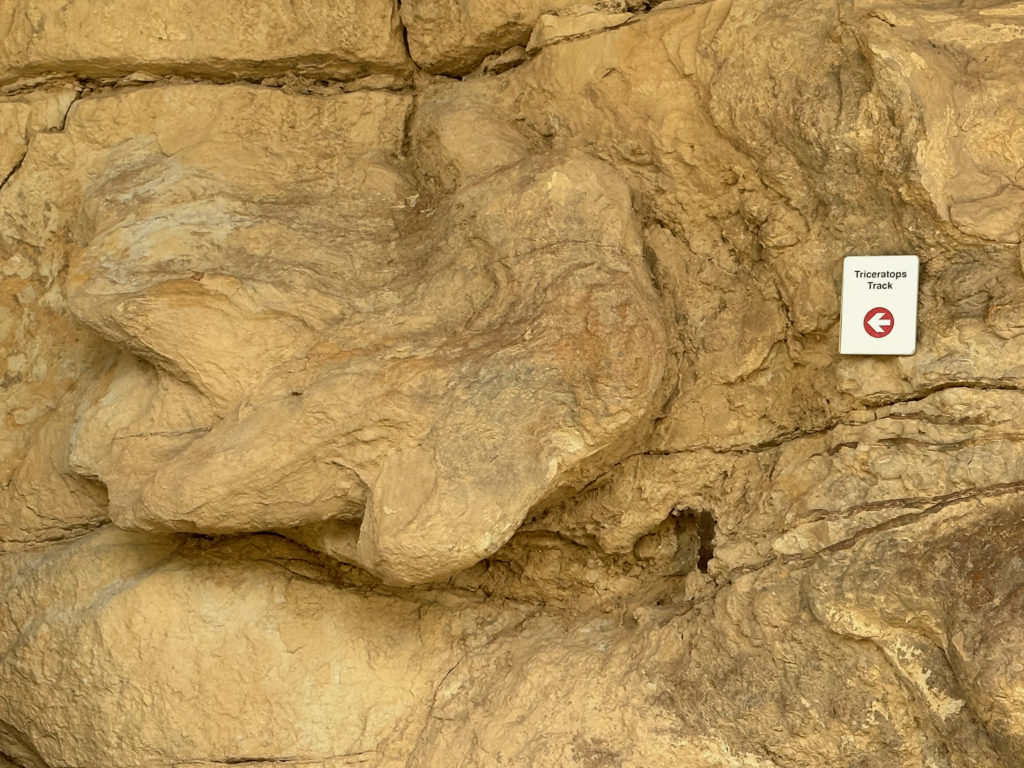

The Triceratops Trail (officially the Parfet Prehistoric Preserve) on the edge of Golden offers an easy walk through former clay mining trenches that have exposed all kinds of interesting dinosaur tracks. Triceratops is confirmed with possible Tyrannosaurus and Edmontosaurus. Easily as interesting are trace fossils of birds, small mammals, beetles, palm fronds, and even (arguably) raindrops. The site abuts an active golf course. It’s a bit jarring to see humans frolicking around the perfectly engineered invasive species of putting green grass, then turning around to face a 100+ million year old wall of dinosaur tracks. I wonder which will outlast the other?
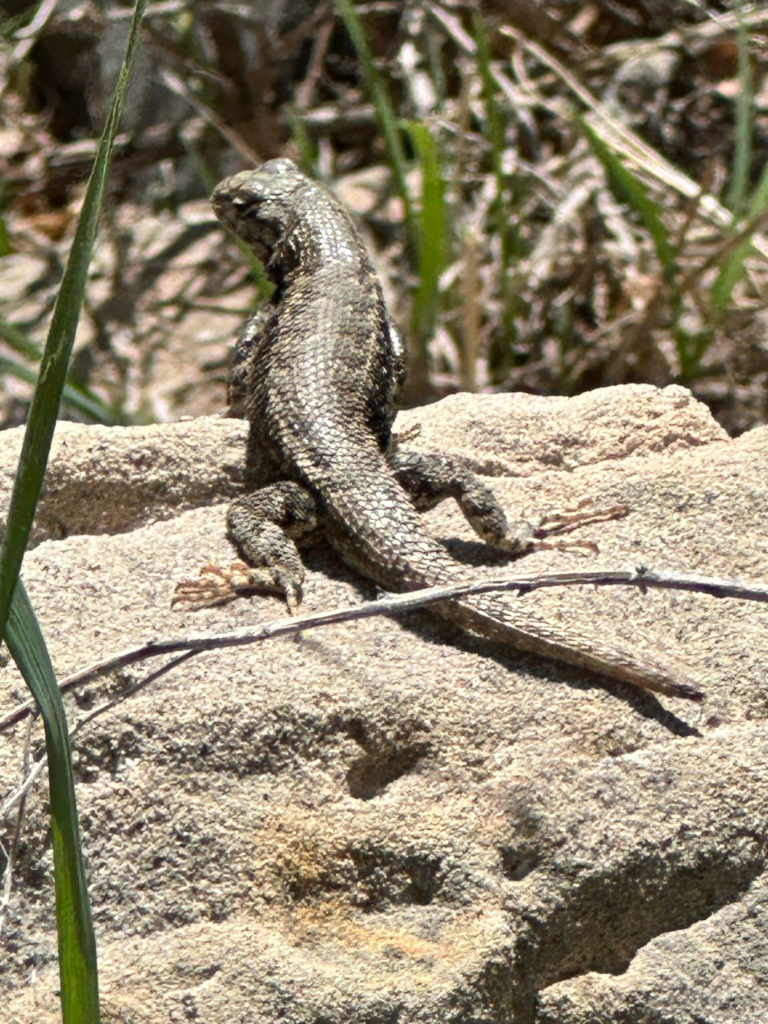

A lizard basks on the Triceratops Trail separated from its clade-mates by a mere 231 million years (evolutionarily). 19th century depictions of dinosaurs took a lot of inspiration from their lizard cousins. We know now that there was very little tail-dragging and tongue-flicking. Our modern dinosaurs are birds and once you note that you can’t unsee it.

In a stroke of geological luck in the Late Cretaceous what was once flat beachfront wetland was jacked up at an angle by two tectonic plates sliding under one another called the Laramide Orogeny. This angling gives us some of the most stunning formations in the foothills (think Red Rocks Amphitheatre) but also provides a kind of outdoor exhibit space perfect for humans strolling by to view all its embedded fossils. One of the best hikes around if you’re into ichnology (the study of the fossilized tracks, trails, burrows and excavations made by animals).

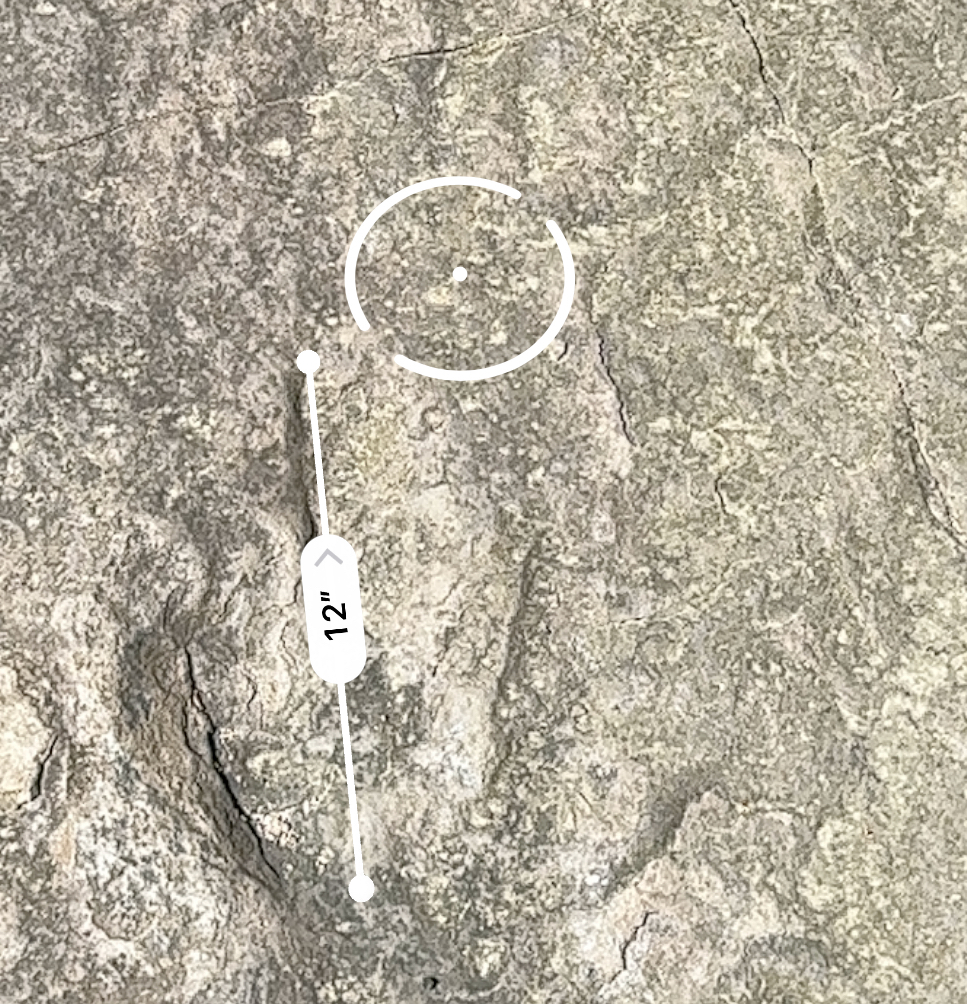
It takes a trained eye (which I do not have) to spot some of these tracks. Points to the curators of Dinosaur Ridge for making the good stuff obvious. Here’s a rare Velociraptor track. That hoop is maybe 4″ in diameter, a reminder that true Velociraptors were the size of turkeys (and feathered like them too). Definitely wouldn’t want to tangle with one, but also not the big scaly door handle-operating baddies from the movies.
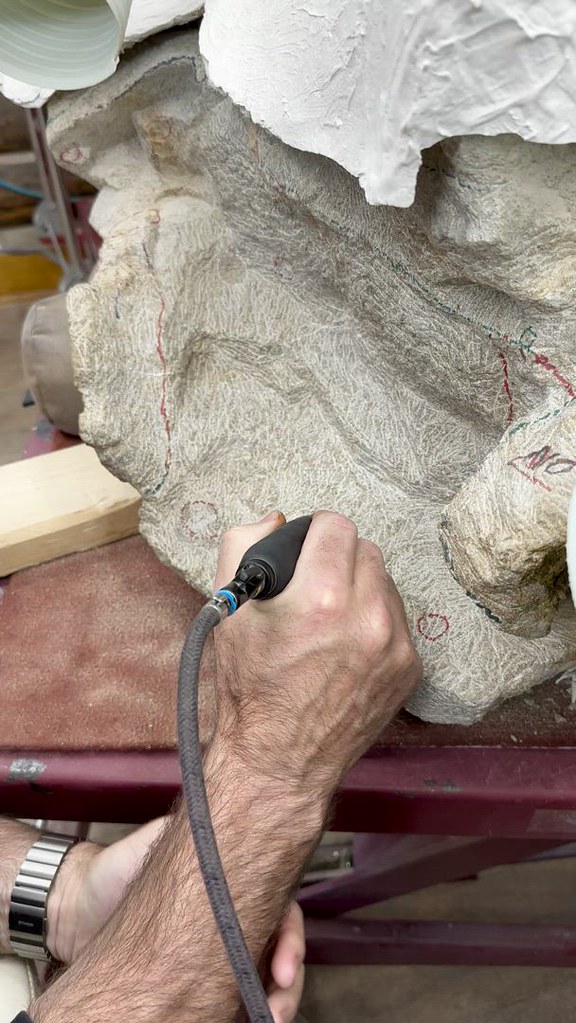

The Morrison Natural History Museum located near Dinosaur Ridge is a standout. Intimate, chocked with great local fossils and full of helpful one-on-one guides (all of whom are city employees — go off, Morrison!), it is exactly what a museum should be. Being mostly the display and preparation facility for fossils discovered over at Dinosaur Ridge, you get to see the real thing. Not many casts here. Highlights include the story of the discovery of the first Stegosaurus nearby, infant dinosaur tracks surrounded by giant sauropod imprints (how did they not get trampled?), an outdoor dig pit, and pointers to plant survivors of the K-Pg extinction. As you can see from the above video, part of the exhibit space allows you to sit down and try your hand at removing rock matrix from an Apatosaurus skull with a dental drill. If you’ve got good eyesight, a steady hand, and an infinite amount of patience, perhaps fossil preparator is the job for you?

In far northwest Colorado straddling the Utah border is Dinosaur National Monument. I visited in the winter so it was just me and the ranger and several thousand jumbled dinosaur bones. The highlight is certainly the “Wall of Bones” which the park has left in situ and built a lovely enclosure around called the Quarry Exhibit Hall. Like Dinosaur Ridge, it’s tilted at a perfect viewing angle thanks to tectonic subduction. All these bones in one place it is pretty confidently theorized come from an ancient stream that just washed them all into one place. Checking off another box on the things-that-appeal-to-John list is that Dinosaur National Monument is an official International Dark Sky site. There’s no artificial light anywhere. Fossils by day, stargazing by night. I must return. (Zoom into the shirt to see the best gift I have ever been given.)
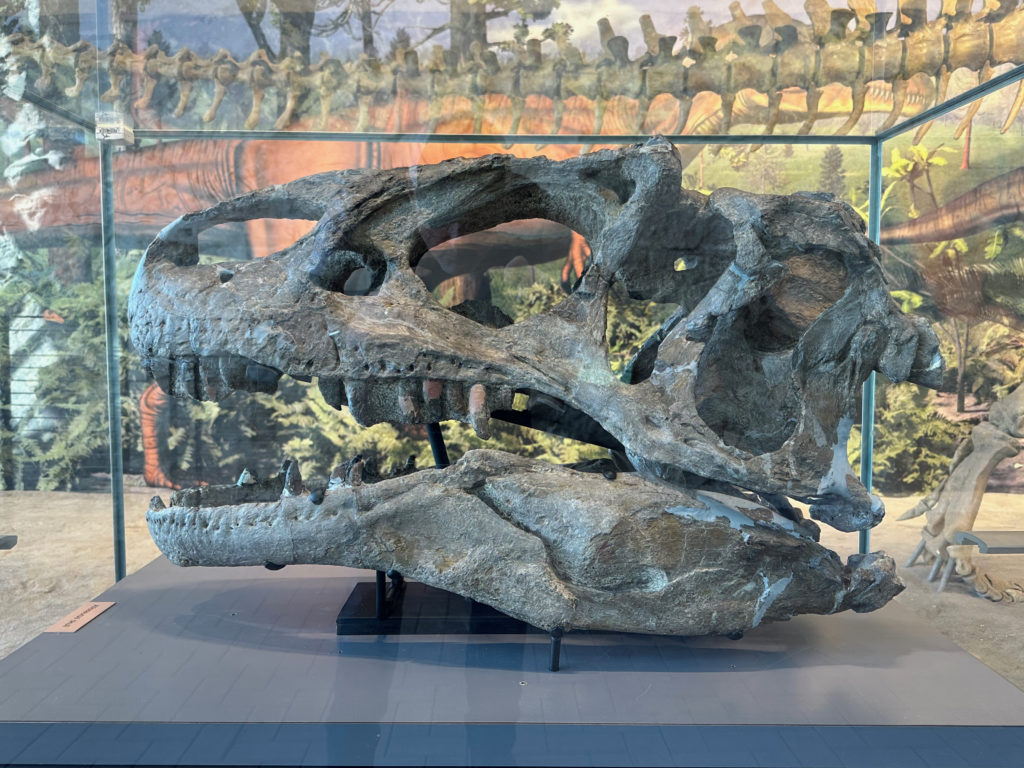

T-Rex gets all the love, but the earlier Allosaurus was every bit the terrifying carnivore, if slightly smaller. Check out the horns on its brow where evolution apparently decided “death machine but more demonic”.
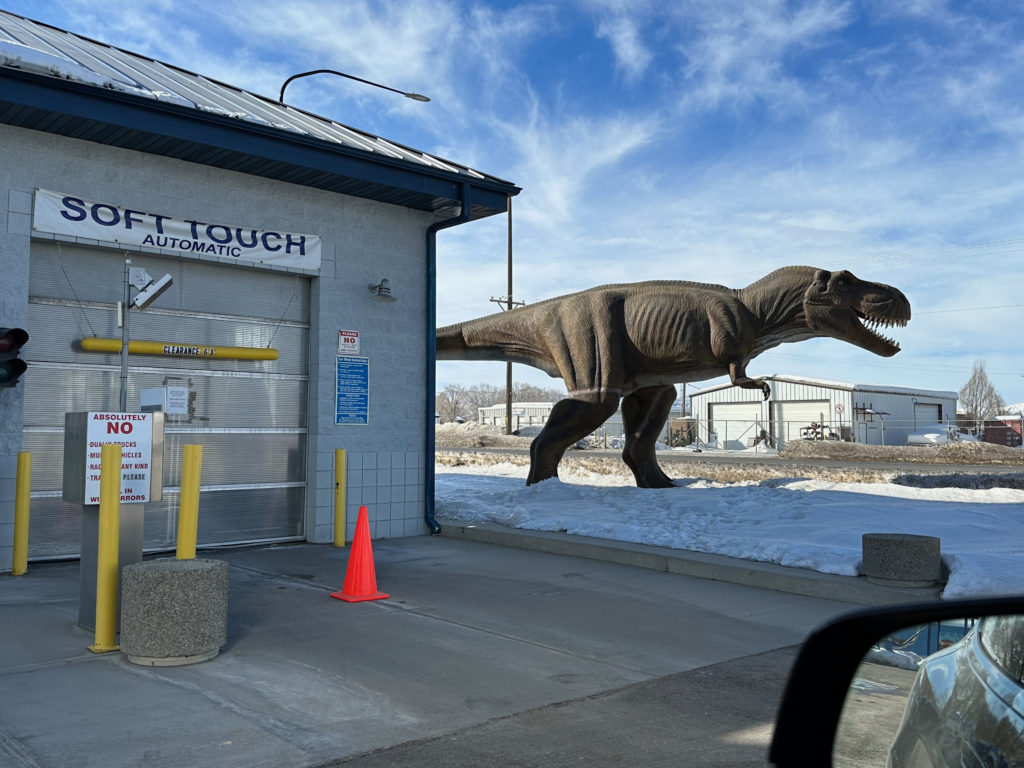

The Colorado town nearest the national monument and formerly known as Baxter Springs renamed itself Dinosaur in the 1960s and they have not looked back. Pictured is a tyrannosaur wanting nothing to do with the soft touch of a carwash. (The town’s counterpart on the Utah side, Vernal, arguably takes its terrible lizards even more — or less? — seriously. Every other business is festooned with some form of fiberglass saurian.)
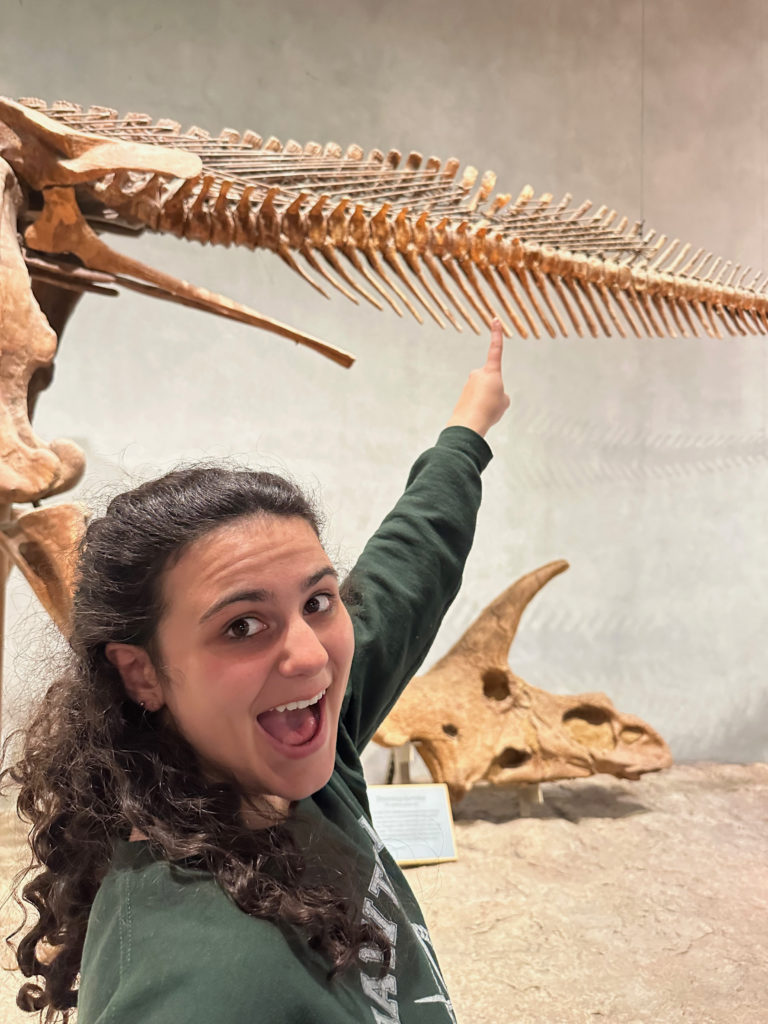

See that missing tip of the Diplodocus vertebra she’s pointing to? Paleontologists agree that’s what happens when a giant theropod chooses you for a meal. This attack would have taken out a sizable piece of tail meat (and of course part of a bone), but clearly the Diplodocus lived another day. That is, until it was entombed in the mineral-rich sediment that allowed it to fossilize and be presented at the Denver Museum of Nature and Science. Bad day for ol’ Diplo, good for us.

Over Grand Junction way the Dinosaur Journey Museum has some striking specimens including a sauropod femur with deep claw marks, properly feathered dinosaur models (which, maybe it was the animatronics, audio, and lighting, but to me floofy dinos are somehow even more chilling than lizardy dinos), and the skull starring in your next nightmare from Diabloceratops. Step back, Allosaurus. Your horns ain’t nothin’. Their working paleo lab, pictured above, was the largest I have seen so far.
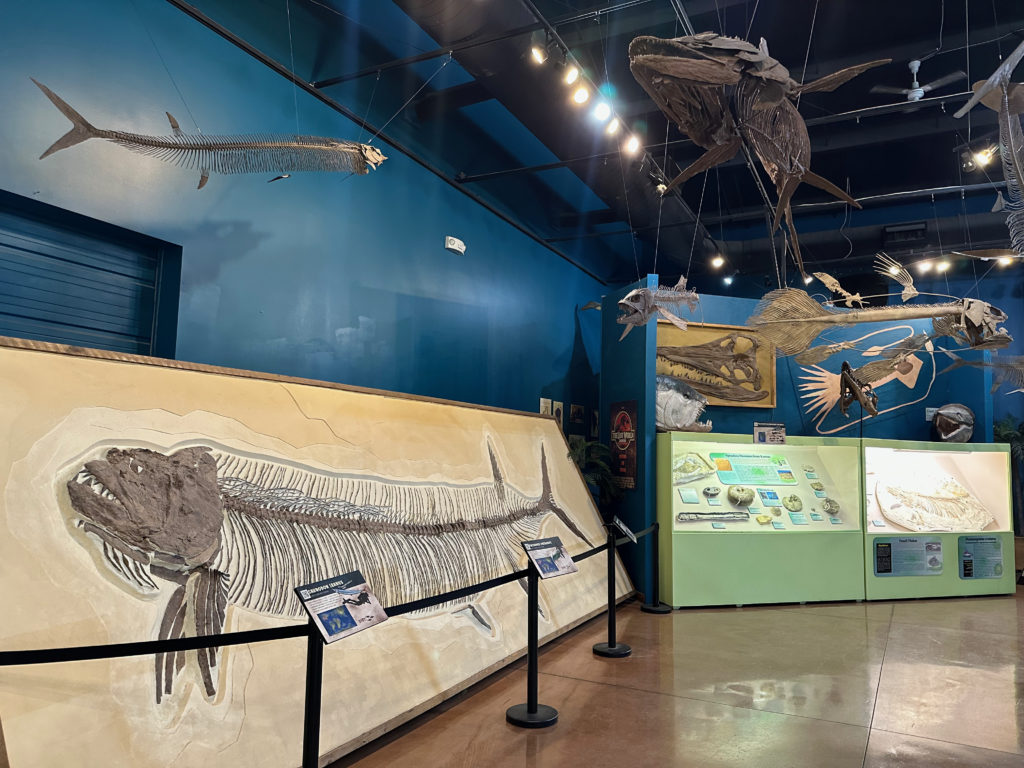

So that Western Interior Seaway whose west coast provided such good fossil-making sediment on its shores also delivers up some incredible marine reptiles and pterosaurs, which, while neither are dinosaurs taxonomically, are related contemporaries and just as fascinating. Most of what’s on display at the Dinosaur Resource Center — located a short way into the mountains up from Colorado Springs — was unearthed by the for-profit Triebold Paleontology company who runs the center, a unique business model to say the least.

All of this is just dilettante paleontology of course. I don’t even know that I qualify as an enthusiast. Admirer, maybe? Paleontology is so radically cross-disciplinary there are entry points from dozens of domains: geology, biology, botany, the visual arts, math, data science, etc. As an example, my son, a physics nerd, was intrigued by our ability to measure footprint size and stride length to accurately calculate pace — a glimpse into not what the dinosaur was but what it was doing. And that’s just extraordinary.
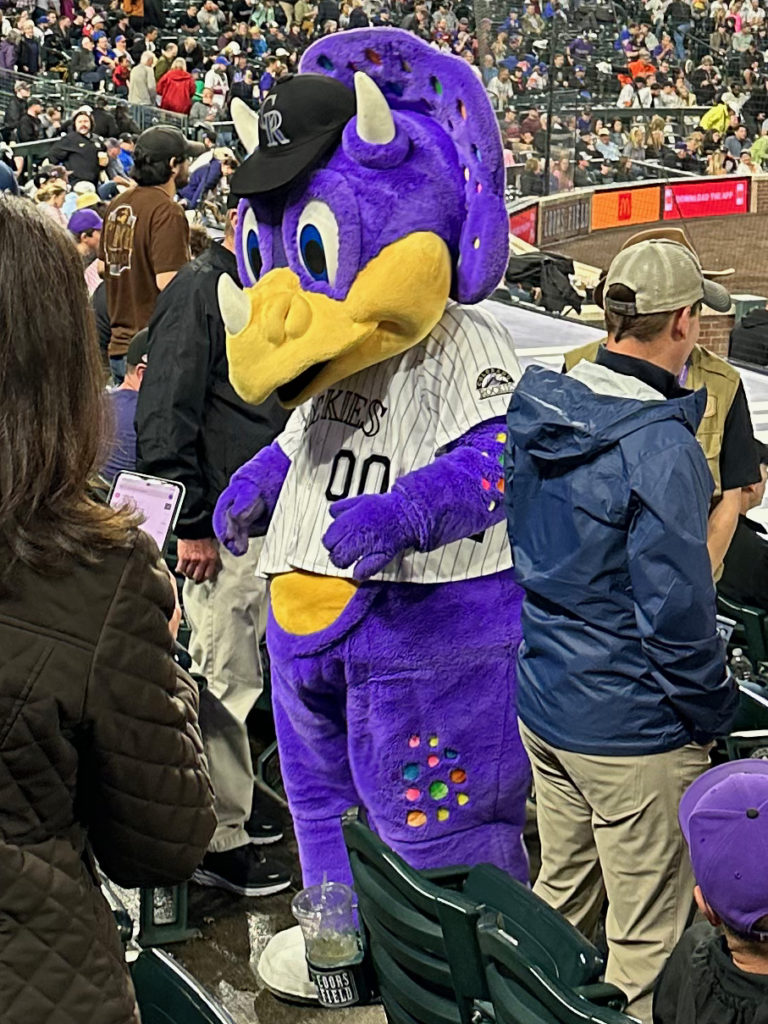

It’s not all about the science, of course. The idea for Dinger, the mascot of the Colorado Rockies baseball team, hatched during the construction of Coors Field when some dinosaur bone fragments were unearthed. It’s impossible to know if those fossil bits came from a Triceratops, though scientists are fairly certain they come from an herbivore (which the ceratopsians were). Somehow Dinger is bipedal, but we’ll let that slide as he’s one of only two (non-avian) dinosaur mascots in all of professional sports.

I’ve found dinosauriana in the strangest places. An otherwise-average Best Western in a Denver suburb with legit fossil casts, vintage paleontology gear, and weekly lectures? Sure why not. How can you not love its murals depicting the feud between 19th century paleontologists Edward Cope and Othniel Marsh of “bone wars” fame? These fellows would actually sabotage each others’ digs they hated each other so much. Immortalized now on the side of mid-tier hotel chain. Nice work, gents.

It’s all gone now, of course. The actual dinosaurs, that is. Paleontology itself is having a bit of a golden age, if the pace of scientific discovery is any measure. But the mindboggling diversity and longevity of these vertebrate marvels ended 66 million years ago. Yes, with a bang, but also likely with a whimper. One ongoing area of scientific research and debate is just how long it took everything to die after that very bad day off the Yucatán. While there are no dinosaur fossils found above the Iridium Layer, the millimeters of strata that make up its layers are measured in millions of years. It’s possible dinosaurs survived for a while after the impact, but what’s nearly certain is that it was radical changes in climate that ultimately ended their particular ecological niche. (Indeed climate change is the culprit in all our planet’s mass extinctions, including the worst one of all which gave rise to the world the dinosaurs inherited.) Today paleontology is not just digging up scary beast bones or fodder for big screen thrills. It’s proof that our global ecosystem is a fragile one, an eschatology written in mineralized organic remains. Towns become ghosts; seemingly invincible living systems become ghosts. Paleontology isn’t about the past, ultimately; it’s a prediction.
If you’d like to delve further I recommend the Apple TV+ documentary series Prehistoric Planet (two seasons so far), the Terrible Lizards podcast, and a few good books.
Holiday Frights 2022

(Of note, I consider Gremlins a Christmas horror movie, fight me.)
Welcome to another annual edition of recommendations for your spooky Christmas needs. (Click here to skip right to the reviews.)
Last year I mentioned the few contemporary remnants of the Victorian-era love of wintertime ghosts, but the linkage between short, dark days and the urge for flesh-tingling storytelling goes back a lot further than that. Shakespeare in A Winter’s Tale (1611) notes “A sad tale’s best for winter. I have one. Of sprites and goblins.” Yule logs, mistletoe, the Christmas tree itself — all pre-Christian celebrations of the winter solstice, symbols of a time for gathering in a space where you could only see to the limit of a fire’s flame. And what to do around this fire, huddled close? Tale-telling, naturally. Those tales, as the setting rather begs, historically have been about ghosts and other haunts. This tradition wound its way into Christianity and the modern era, as Colin Fleming notes as a series of
… readings for the season—but not really of the season … a rather more pleasing terror—the ghosts, even when they mean to avenge themselves upon us, also seem to have dipped into the nog a time or two, with their own playfulness in evidence. Sure, they can kill you, but they do so with a joke or two at the ready. These are the short days of the year, and a weird admixture of pagan habits and grand religiosity obtains. There is also booze. People didn’t have TVs: people drank, people got to telling tales, someone told a tale and someone tried to tell a bigger one, and then, lo, we got a whole ghost story Christmas tradition.
Holiday ghosts were fading away by the early 19th century until Charles Dickens famously brought them back as time-traveling tour guides in a grand morality tale. A Christmas Carol is the last major vestige — a tomb marker, if you will — of a tradition that was far weirder and scarier than any of Dickens’ four ghosts. And yet, A Christmas Carol is part of the cultural atmosphere of Christmas, there even when it isn’t in the foreground: scrooge-as-a-verb, being shown how behavior can spawn multiple timelines, the inspiration for the Grinch, and countless adaptations (including this year’s Spirited with Ryan Reynolds and Will Ferrell — worth a watch). It’s embedded in our childhood psyche in a way unlike any Halloween ghost story.
Here’s my personal proof. Christmas Day, 1982. My siblings and cousins retreat to the basement to create our own adaptation of Dickens’ classic. It was the dawn of VHS cameras, the noonday of wood-paneled suburban decor, and the dusk of my short career as a playwright. This grainy, budget-less masterwork, a Christmas gift to you, will likely be the most disturbing thing you watch as a result of this newsletter.
You may think that Halloween has the monopoly on horror media, but it isn’t even close (at least in the USA). There are hundreds, possibly thousands, of Christmas-themed horror movies from barely watchable home movies (ahem) to legit masterpieces — the true legacy of those bards of yore and their campfire frights. Let me tell you about some.
An update on the Marhaver Lab campaign
I turned 50 last month. It’s a funny age. Old for sure, but not ancient; closer to the end than the beginning, statistically. Maybe because of that memento mori I seemed naturally to be thinking less about the present and more about the future — a future far enough out that does not include me. And that got dark real quick given the state of our planet. In an effort to keep it light I wanted to do something that focused on the long term, something (however tiny) that contributed to the foundations of a healthy planet.
Enter Dr. Kristen Marhaver. I first met Kristen years ago after an Ignite talk she gave at the ORD Camp unconference. The whole talk was jawdroppingly insightful (and funny), but I remember one moment especially. She was describing the process of coral sexual reproduction, a not well-understood event that happens at night, whereby coral simultaneously release sperm and eggs into the water. These particles are positively buoyant so they all come to the surface. Kristen continued that the evolutionary brilliance of this is that the buoyancy effect turns a geometrically complex insemination problem in three dimensions (everything just willy-nilly colliding in the open water column) into a much more manageable two dimensional problem at the water’s surface. But here’s the real beauty: fertilized eggs then become negatively buoyant ensuring that they fall back to the substrate to try to grow and thrive. You go, evolution!
So, yeah, I’ve been interested in the science of coral reefs for a while. Following Kristen’s work, scuba diving reefs all over the world, and running my own little experiments at home — not exactly a side gig, but certainly a passionate avocation. Running a small fundraising campaign for Marhaver Lab to celebrate my 50th birthday seemed a natural thing to do.
I had no target in mind when we launched the project. Indeed, if anything I thought worst case a low raise would quantify just how few friends I had left after a pandemic. But, in a little over a week we raised just shy of $11,000 — far more than I could have hoped for. Family and friends donated (thank you!), but what really became interesting is how the campaign evolved in a few days to receiving support from people neither I nor Kristen even knew. The word got out, apparently, and people love baby corals.
I think no one loves baby corals more than Kristen, though. If you’re interested in the work she does, there’s a just-published piece on a “moonshot” project she was part of to cross-breed Elkhorn coral (Acropora palmata) from Curaçao with the same species (exhibiting different environmental characteristics) from Florida. This is important as we look for ways to introduce heat-tolerance and other forms of climate resiliency into reefs worldwide. It’s called “assisted gene flow”. Basically Kristen’s a midwife of the coolest sort. And yet, as this excerpt notes, there’s still work to be done:
Marhaver thought that they had a five to 10 percent chance of success. To have hundreds of healthy coral now sitting in tanks barely crossed her mind. Conservationists are more attuned to the vibrations of endangerment, extinction, and loss. To have a moonshot succeed is unfamiliar territory. With the impossible now possible, the next hurdle is moving from the lab to the ocean, a leap that not everyone is comfortable with.
$11k isn’t a lot of money given how much it costs to perform the kind of lab-based and in situ work that Marhaver Lab undertakes. But it’s a start and more than that it’s a signal that a lot of people care about the complex interdependence of our planet’s health with even the smallest living creatures. I may not be ancient (yet) but coral organisms are and their well-being is inextricable from the well-being of our global marine environments. If the oceans fail, we fail. Venus is too hot. Mars is too dry. We have to make this third rock work.
One day at a time

Friends! I turn 50 years old on August 4. I’ll pause for old person jokes, but please speak up.
50 is an arbitrary milestone, sure, but I got myself a pretty great gift and I’d like to tell you about it. August 4 will mark 1,000 days since I gave up alcohol. It’s been the best thousand days of my life overlaid right on some of the worst thousand days we’ve had as a human species (battling a virus species). That this sobriety milestone happens on my 50th birthday is a coincidence. But maybe there’s no such thing as a coincidence?
The story of my road to sobriety is a long one, one I am happy to share at length with anyone — especially those whose relationship with alcohol is unhealthy. Here’s the short version: I accepted that I had a problem with alcohol — let’s call it what it is without stigma: alcoholism — just after Halloween 2019. Halloween is my favorite holiday of the year and also my son’s birthday. So, naturally, a terrible time to crater. But crater I did, which was exactly what I needed. Went away for help for quite a while … and then the pandemic happened and I came home to a new life. The world was in lockdown, but I felt fully unlocked. It was especially eye-opening time, those early days of sobriety, when the world itself was coming to terms with the lessons of recovery: re-connecting with simple life-affirming things, not projecting too far into an unknowable future, living one day at a time and chalking those single days as victories. It was as if all of society for a brief period was supporting my own early, delicate recovery.
It’s no longer early; it’ll always be delicate I suspect. So’s life. But each day is a great day and that feels better than any buzz ever did. Not gonna name names, but I have received a lot of help and love from family, friends, and then-strangers in this journey. You know who you are and you know how much I appreciate you.
To alcohol I say, no hard feelings. We just didn’t work out, you and I, when I realized I didn’t love you. Totally cool with your relationship with others. Best of luck!
So, yeah, one day at a time adds up. Sometimes it adds up to 50 years (thanks Mom and Dad!); sometimes it adds up to 1,000 days of clean living. I intend to keep adding.
Why am I telling you this before my actual birthday? Because I got myself another gift: this fundraiser for a cause very close to my heart. 🪸
The Marhaver Lab — run by marine biologist, science communicator, Georgia Tech grad, and friend Kristen Marhaver — is a research outpost based in Curaçao in the southern Caribbean. The work of Marhaver Lab is aimed squarely at helping solve the problem of declining biodiversity of the world’s coral reefs. This is critical work: coral reefs are foundational elements of our oceans’ larger ecology. When reefs thrive, fish populations thrive. When fish populations thrive, the planet (and humanity!) thrives.
I don’t think anyone gives gifts for a person turning 50, but if you’re so inclined your support of Marhaver Lab would mean a lot to me. More information and tax-deductible donations accepted here.
Thanks for reading! Hope you can donate. On to the next day, with gratitude!
Gravid With Decay, love letters to a genre

Hello friends! Last year when the lockdown started, I watched a lot of movies. Most of these were what’s considered horror or closely adjacent to it. I wrote about almost everything I watched (and why I think it was as much an immune response to the pandemic as antibodies).
That long post, though, was the summation of months’ worth of biweekly emails sent among friends just sharing recommendations and thoughts on movies we were watching. I loved writing those and was kinda sad when we wound it all down.
Welp, we’re not out of the pandemic and I’m not done sharing short thoughts on horror via email. Like any good monster, the reviews are back, undead. Also like any good monster, you never quite know when it will appear (OK, fine: never more than weekly). Sign up at Buttondown or below. (Need a preview?)
Cityfi: yeah, it’s a verb
Cityfi? Like Wi-Fi? Or like … unify? Is it a thing or an action? I’m here to tell you it’s a verb. Everything about the work Cityfi does is about motion, progress, and change. So here’s a little update on my movement, as I take leave from this small but mighty company.
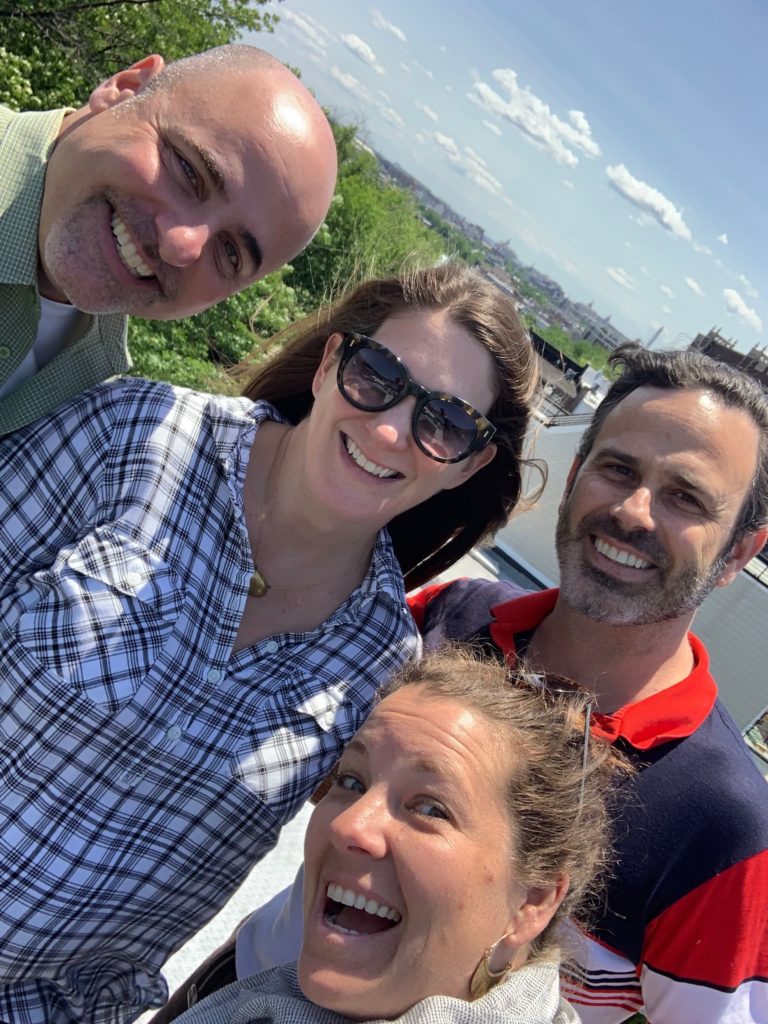

July 2016, Before Times: my family and I had just arrived in Denver after a cross-country relocation. It was a fresh start geographically but also professionally. With my friend and former colleague at the City of Chicago, Gabe Klein, we started a new company with the amazing Ashley Hand. It was the birth of the urban change management consultancy Cityfi.
Our hunch that both the public and private sectors could use guidance navigating the rapidly-evolving realms of urban mobility, data analytics and privacy, equitable services, and climate change resiliency (to name just a few) was proven correct. We were off to the races and working with great clients all across the country and globe.
Cityfi is stronger than ever now, coming up on five years in. With the addition of partner Story Bellows and some amazing senior staff, we’ve created a first rate team, a portfolio of work, and most importantly a reputation for responsive, thorough consultancy that seems to be needed more than ever.
There’s never a great time to move on from something you love. (I know this; I left Chicago … just as the Cubs were about to win the World Series.) But now’s my time to step forward from Cityfi.
Obviously this has been a past year of change and uncertainty, but for me the relative slowdown of life — limited physical interaction and travel, whittled-down life patterns — has brought what I think is clarity of purpose, or at least time to listen with less background noise. The signal coming through isn’t completely decoded, but I’ll let you know what it says when it is.
For now, I have a class to teach and a brand new smart cities certificate to help manage at the University of Colorado Denver (as, ahem, a scholar in residence). I remain involved locally as the board chair of the Colorado Smart Cities Alliance (an early Cityfi initiative and one of which I am most proud).
While that pride exists for a lot of what we built at Cityfi and I’m confident that its future is bright, the main emotion I feel is gratitude. I am not sure I could have made the transition to a new life in Colorado without the support of my partners. For that I am immensely grateful.
Lastly, deep thanks to the clients, associates, and affiliates who made these past years of work engaging and meaningful. Thank you all for treating Cityfi as a verb. Here’s to your continued movement — healthy, happy, and ever-forward.
Coral brickscape
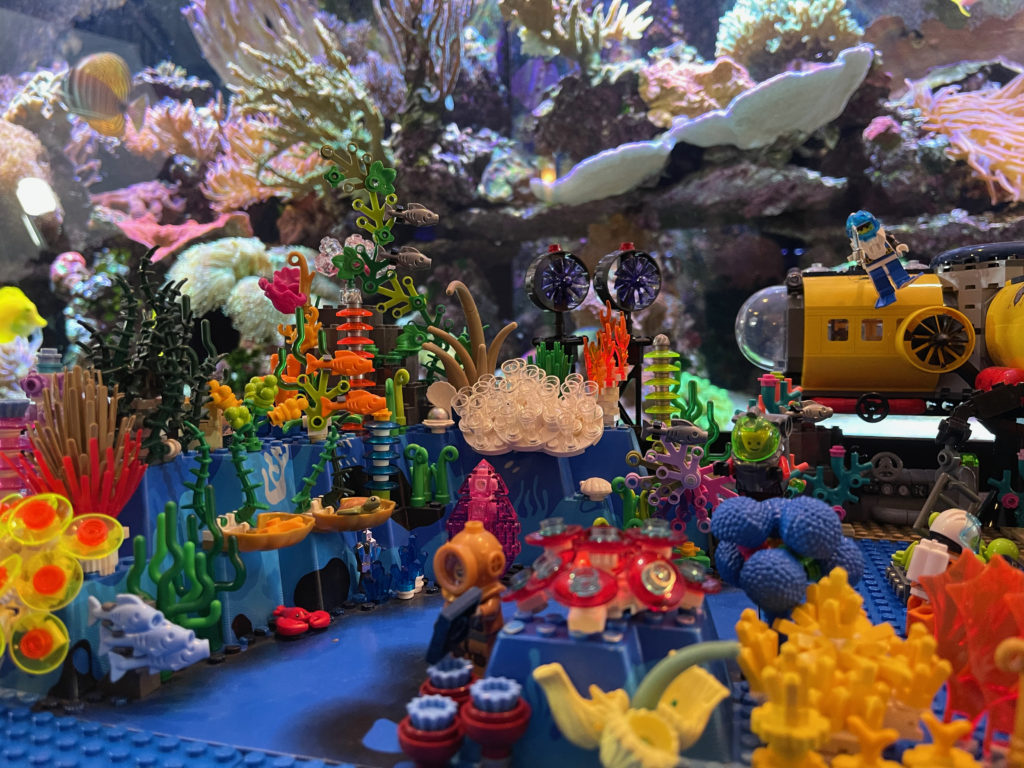
I’m a coral nerd and an unrepentant adult fan of LEGO bricks, so I figured why not attempt a completely instruction-free build of a squishy, curvaceous reef out of hard plastic 90° angles.

Certainly I get the irony of making a model of corals from non-biodegradable plastics, but maybe that’s the point (and part of the point of keeping a huge tank of actual corals): the need to create a microcosm of something that’s rapidly disappearing seems more urgent, even if it’s only a creative pastime.
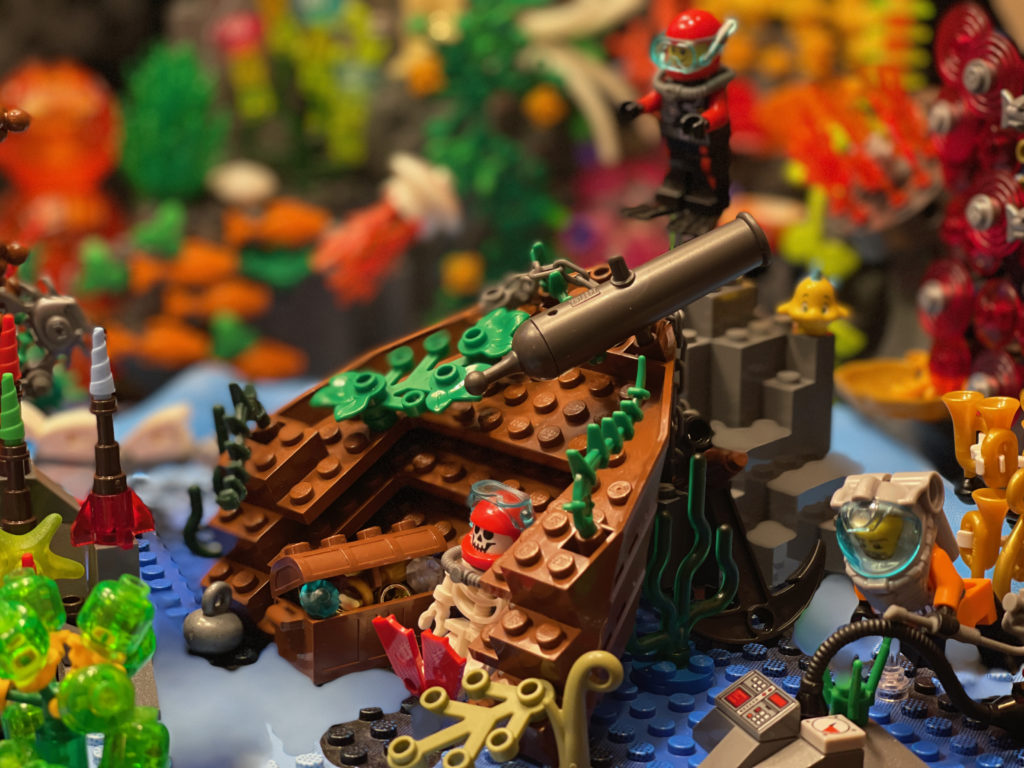

And what a pastime it was. Early on in my musings of how to do this I realized there was no way I could find the bricks I thought I needed just sorting through the 100,000+ loose bricks in the dozens of tubs and bags they were randomly collected in. This launched an effort at organization and general de-crufting that deferred the actual reef project for months.

The sorting itself was, in a way, part of the design process. Touching every single brick we own (in every possible orientation, decontextualized from its originally-intended purpose) gave me a millisecond per brick to consider how it might be used to simulate the crazy shapes that reefs take.
And that was the real challenge; there’s nothing rectilinear about coral. If it isn’t a swaying mass of tentacles, polyps, and pulsing mouths it’s a bleached Iron Throne of jagged, fractal CaCO3. I took a lot of inspiration from techniques for making botanical models (plants, flowers, etc) but also from the advanced facade decorations included in LEGO modular architecture sets. Basically, I catalogued as many of the ways of getting bricks to assume odd or semi-random angles while still being affixed to one another. Didn’t hurt that I could just stare at my own tank of beasties for inspiration when I got stuck.
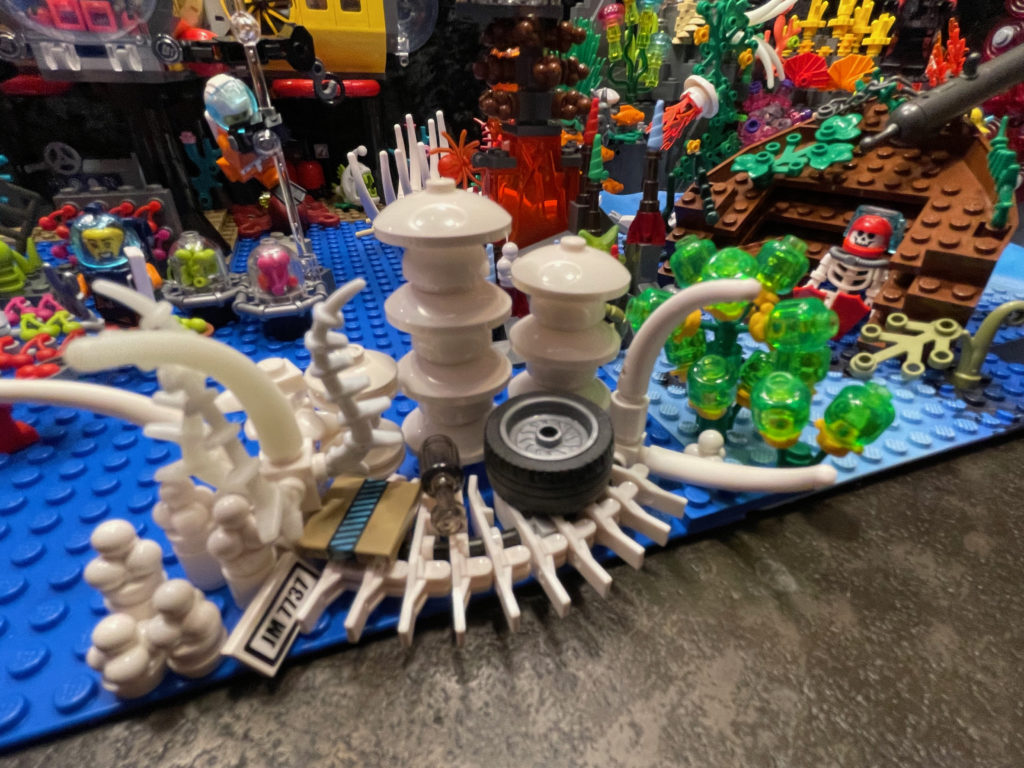

There is an actual LEGO coral brick, but I ended up not using it much as it’s really a distillation of what we generically think coral looks like. In the end it was far more fun to repurpose minifig hairpieces, radar dishes, trumpets, chalices, carrots and ice cream scoops. Mounting all that was mostly an exercise in SNOT (“studs not on top”) design, using nearly every brick made specifically for that purpose and a ton of techniques culled from the LEGO nerdweb.
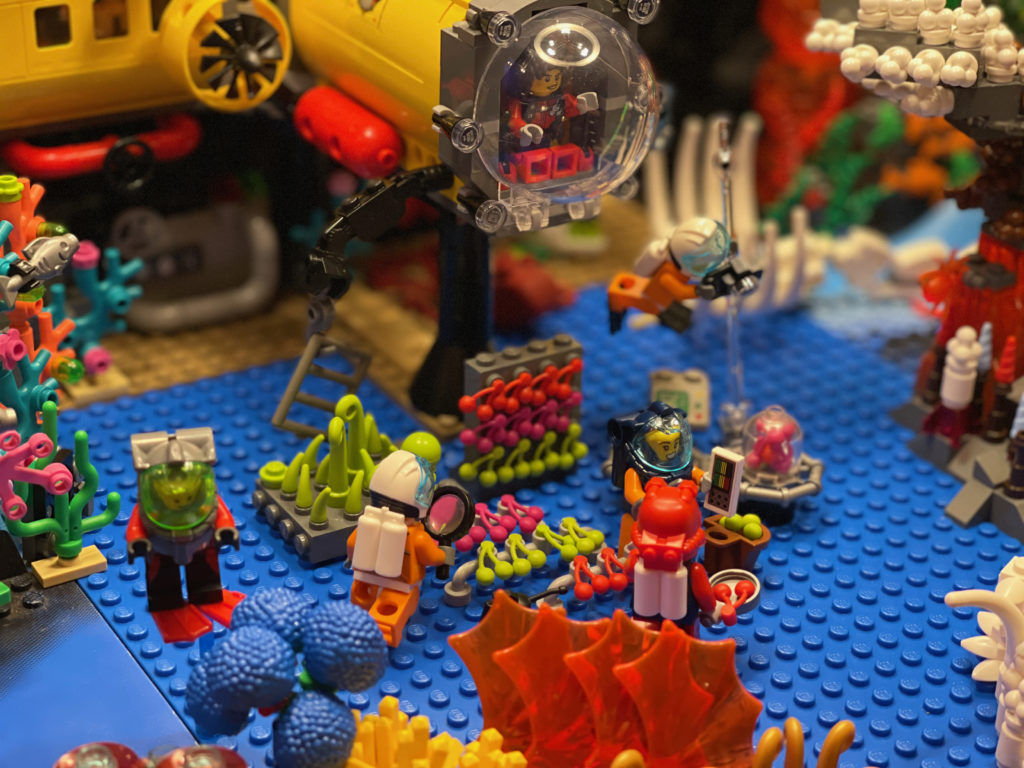

There’s a lot going on in this ecosystem. The main subdivisions left-to-right are a vibrant reef section, the marine science and bleached reef middle section, and the “all the things on the seafloor” section which includes a shipwreck, hydrothermal vent, and whale fall. Other items include a transoceanic fiber cable (with repair technician attempting to bring broadband to your continent), wreckage from Oceanic Flight 815, Aquaman fighting Black Manta, a couple shy mermaids, the Antikythera Mechanism, a diver as skeletonized as the whale, human trash in the bleached patch (including an actual broken piece of ABS LEGO plastic), and a steampunk Diver Dan. See if you can find them all. (Here’s the full set of photos at Flickr.)
It’s all now mounted on a lower shelf in my home library, part of a larger cityscape and sea. The ocean surface needs a lot of work, but for now I’m going to turn to the relative comfort and trance-like ease of building a set with actual instructions. Freeform and organic is a lot of work, you know?
What I found digging through 41 years of LEGO bricks
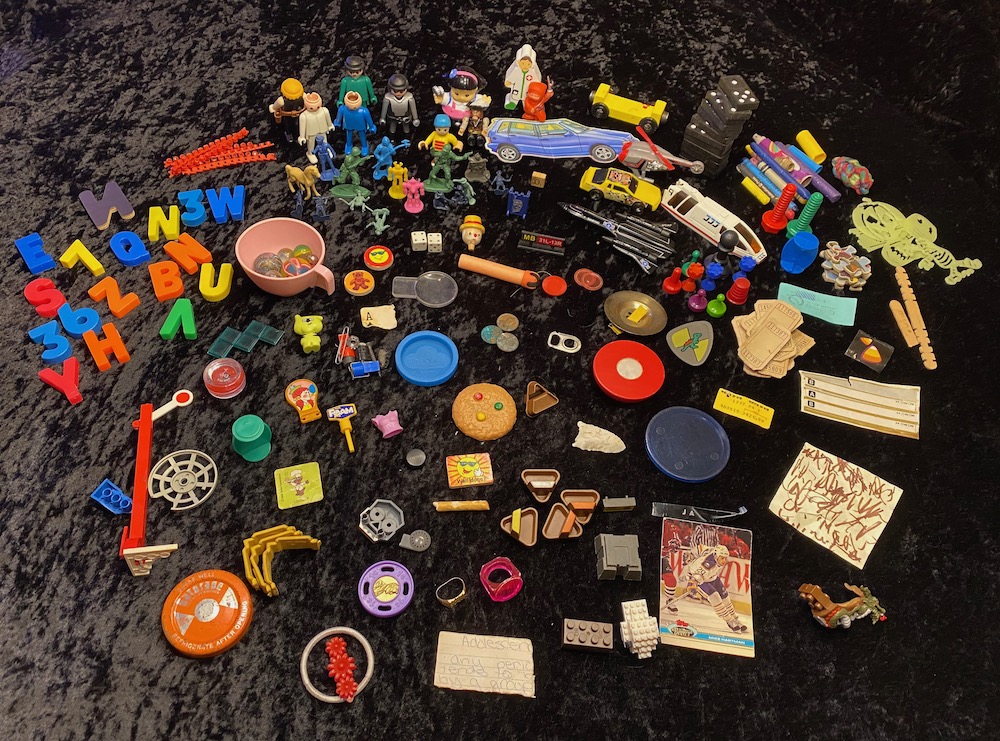

A few months ago I embarked on the Sisyphean task of organizing the LEGO collection in our house. I mean, let’s be truthful: it’s my collection, but my children have historically been the happy recipients of sets that I have ultimately folded into the larger pile of bricks over time. And what a long time it has been collecting, disassembling, and pretty consistently enjoying this big mess of ABS plastic.
My first memory of a LEGO set is the Galaxy Explorer from 1979 (which I rebuilt a few years ago). Since then I’ve never consciously thrown any bricks out, though certainly some have been lost and many have been broken. Using weight as a rough approximation for quantity we have well over 55,000 loose LEGO pieces. (Closer to 100,000 if you count pieces actually residing in built sets and MOCs.)
The actual sorting through all that has been fascinating and therapeutic, equal parts mind-numbingly meditative and joyful. But perhaps the most interesting part of this whole process has been sifting out all the junk in the bins that is not LEGO. And there was a lot of it, specifically 8.325 lbs of accumulated detritus of my youth (with some pieces from my kids’ younger days too). Sieving through it was a kind of autobiographical archaeology, a forensics of youthful amusement.
Inspired by Amsterdam’s dredging of a few canals to install a new subway line where they uncovered and displayed centuries of things from everyday life, I thought I’d lay out a small selection of the non-LEGO trove here. It’s an incomplete picture of how I grew up, but a picture just the same.
- metal Gatorade cap from when it was sold in glass bottles
- Native American arrowhead from a felt display box I had from a trip out west — easily my favorite find
- Ace of Spades, mutilated
- Playmobil figures, many balding as I am
- Little Green Men and various figurines of people shooting things
- Play-Doh container cap
- hair barrette and tie (my sister’s)
- toy rings
- dice
- magnetic refrigerator letters
- spent toy gun caps
- all manner of broken LEGO
- counterfeit LEGO
- game pieces — I think The Dark Tower is in here, loved that game (which is coming back!)
- puzzle pieces
- hockey playing card — of note, I never followed hockey in my youth
- air hockey puck — also of note, we did not own an air hockey table
- lip gloss — possibly mine, probably my sister’s
- marbles and bouncy balls
- pennies with a lot of verdigris
- tickets (likely from Showbiz Pizza)
- a Paris Metro ticket (huh?)
- cassette tape labels — used, naturally!
- dominoes
- note fragment in what I think is my sister’s handwriting: “Adolescn .. any perio … tends to b … by a group”
- embossed label strip — loved those things
- post-it note w/ scrawl — looks like testing a marker
- a Toys ‘R’ Us tag for $29.99 — wonder what that was?
- various stickers
- a thimble
- lotta crayons and writing implements
- Matchbox car and USAF Blackbird
- toy monorail — transit, baby!
- Nerf dart
- a magnet that has pulled together random metal bits
- an Enter key
- a half-gnawed pretzel stick, easily 30+ years old
- part of a in-ear headphone
- other unidentifiable cruft
Not exactly panning for gold, but there’s definitely a Toy Story-esque nostalgia at play. Literally play, which is the only consistent throughline with all this junk. My youth was certainly filled with electronic gadgets, video games, and computers — but none (or very few) of those have lasted. What remains in this re-assambled time capsule are the simpler items, perhaps the best items. A collection of fragments shored against, if not ruin, then the ruinous loss of innocence. I’m not throwing any of this away.
Hair of the dog: some notes on movie-watching during the pandemic
You know how a vaccine is really just a little bit of the same thing that makes you sick in the service of building your defenses against the thing? OK, good.
There are lots of people seeking respite from the real world this crazy year from TV and movies that take our minds off the horror of the virus, racial inequity, economic tumult, and climate change-fueled catastrophe. But an article from a peer-reviewed journal I stumbled upon a few months back — Pandemic Practice: Horror Fans and Morbidly Curious Individuals Are More Psychologically Resilient During the COVID-19 Pandemic — makes the argument that fictional horror may actually be psychologically useful during this time, if not palliative then at least preventative.
I surely don’t need scientific rationale to watch a horror movie but, as it happens, my intake has increased noticeably since the earliest days of COVID-19. Whether that’s lack of travel or much of anything to do outside the house or some deep-seated need to build resilience as the article discusses, who knows? But I’ve been sharing short reviews with friends since May and thought you might like them too. (Mostly movies and television series with a few books, comics, and video games thrown in.)
78/52 is a documentary about a single scene in a single movie, Psycho‘s showertime. Sometimes horror changes the cultural imagination permanently.
Sea Fever is your standard trapped-in-a-confined-vessel-with-a-horrible-infection feature. Except with Irish fishermen and a pretty great, f***-your-superstitions female lead scientist. There’s an environmental message that wants to get out. Never quite does, but the nasties do.
A Dark Song is an excellent, weird flick about an arduous occult ritual. Two people locked in a house for months. Excellent performances. What I thought was a somewhat cheesy tableau at the end actually continues to haunt me.
Carriers ages pretty well. Post-viral outbreak. Chris Pines early in his career. Not stupendous, but super on-point.
Related, I may be late to this, but Reelgood (app and website) is changing my life. Integrated across all video services, it’s a log of what you want to see and what you have seen.
Monster Party was a delightfully random find. Premise: upscale home dinner party for recovering addicts. But their addiction is gruesome. Subplot: three teenagers hired as party waitstaff who are really thieves intending to burgle the place. Tight film, gory kills, and there’s also a sub-subplot that had me wondering how it fit the whole time.
Wow, Bloodsucking Freaks. Ever seen A Serbian Film? If not, don’t, but if you have, this film exists in the same universe of WTF. Grindhouse sleaze at its best. No idea how this was ever released back in the day. Premise: Theater of the Macabre achieves dramatic realism by doing for the stage what snuff films do for celluloid. Also: every woman in this film is naked the entire time.
As documentaries go, To Hell and Back: The Kane Hodder Story, was pretty good. Hodder wasn’t the original Jason, but he was the iconic Jason. His story is interesting, especially the part about setting himself on fire accidentally and suffering far more than he should have recovering from it. (There’s also a Tom Savini documentary out. I had no idea his connection to Pittsburgh and the original Night of the Living Dead!)
Ever watch a movie you’re pretty sure you have seen before and even when it’s over you’re not sure if you did? Well that was me with Absentia. And maybe that’s the point of the movie itself. Premise: husband goes missing and is declared officially dead after seven years by his wife. You’ll never guess what happens next. Mike Flanagan directs and you can see the beginnings of the creepy-as-shit blocking he used in The Haunting of Hill House. (If you have not seen that remake, you should ignore all the other recommendations here right now and go watch it.)
A guilty pleasure. I love The Last Drive-In with Joe Bob Briggs. It’s a double-feature every Friday night while the season lasts (also on demand of course), though the live part of it makes social media actually fun. Joe Bob provides commentary every 20 minutes or so. He’s a redneck, he’s wickedly smart, and he loves horror. Diverse selection of films including many whose covers I admired in the VHS rental shop growing up but never actually watched.
There’s a show on the Travel Channel called Portals to Hell because … demons have wanderlust? I would not know this except that the show was profiling a house near me called The Croke-Patterson Mansion. Absolutely standard — no, sub-standard — “reality” ghost-hunting crap. And yet, having a neighborhood portal to hell is super convenient. (The real horror of this was the live Twitter feed during the show. An online wannabe parapsychologist convention, basically.)
More environmental horror, Underwater is a less hopeful version of the Abyss with better effects. 7 miles underwater with no zombies per se, but lots of things that will kill you. Like, being 7 miles underwater. First on-camera death is pretty great.
Hard to watch (at least for a parent of teenagers), The Dirties is whatever the found footage genre has grown into about two bullied high schoolers who make a documentary about being bullied and then decide to do something about the bullies. Not horror at all. Have we decided that Troubling is a genre unto itself?
The Apostle is like The Village with no twist ending or The VVitch without Black Phillip. But it does have a pagan vegetal sorceress. Welsh horror, folks. You heard it here first.
Rise of the Gargoyles is a terrible (TV) movie. I was legit surprised at one of the kills. Still awful. Worth watching. But it’s bad.
A few weeks back I watched the entire Resident Evil franchise. The first one is the best, in my opinion. It aged less poorly than many of its more recent sequels. Gimme an undead flick or a creature feature any day but not at the same time. I do like the idea of yoking together zombies and sci-fi elements. If you do too, I highly recommend the game Dead Space. Essentially, a first person what if Resident Evil but more Event Horizon-y. Playing this with my kids when they were way too young is simultaneously one of my lowest moments as a parent and some of their self-admitted fondest memories.
Blumhouse’s newest re-imagining of the Universal Classic Monster back catalog, The Invisible Man, is really quite good. Most disturbing emotional/domestic abuse film I have seen since 10 Cloverfield Lane. Especially relevant given the truly horrific scenario we’re in with the lockdown-driven rise in home abuse. More sci-fi than the original, still super creepy. Basically the apotheosis of Leigh Whannell’s line from Insidious: “It’s not the house that’s haunted.”
Blood Quantum is Native American horror, something I do not think I have ever seen — at least not done from an indigenous perspective. Awesome plot point: in a reversal of the disease-based genocide inflicted by the European conquest of the New World, Native Americans are immune to whatever has turned the rest of the world into zombies. They are not, however, immune to being torn apart by them. So American Indian reservations become fortified sanctuaries against the onslaught. Amazing kills, amazing film — especially in a pandemic.
Fantasy Island coulda been great, but it wasn’t. My youth was shaped in part by the original Fantasy Island (and its Saturday night double-feature The Love Boat — also a great target for a horror re-do, come to think of it). Rare that Blum swings and misses, but this one was so convoluted and Michael Peña so hard to accept as a bad guy, that it just didn’t gel. Live your fantasies, pay the price is a great construct though. Can we get a do-over?
Took a while, but I finally watched Mandy. This is just a stunningly beautiful film. Scandinavian death metal liner note art come to life. But as a revenge flick it is just so-so. Nic Cage is of course an exceptional rage-filled lunatic and the cult members are suitably weird. I Spit On Your Grave wins by the landslide in this particular genre though.
What did we get from Get Out besides a phenomenal film? We got this great documentary: Horror Noire: A History of Black Horror. A mix of scholarly and first-person accounts from actors and crew, I learned a ton. Like so much horror, the positioning of of black characters in film through time maps to larger social forces: black as the scary Other, black as disposable, black as retribution for the sins of white. Get Out looms large, but so does Candyman. Lots of great stuff I had never seen too, Blacula in particular and this one …
The Girl With All The Gifts is basically the game The Last of Us (if you’re familiar) with great acting performances. Fungus-based infection turns people vicious and feral (but not, I think, undead) and ultimately into compost for spores to grow pods. Super creepy wide shots of the infected when they are not feasting — not ambling around Walking Dead-style, just standing motionless. Glenn Close is fantastic as is the young female African-American (British?) lead Sennia Nanua. She’s infected but second-generation so basically normal, unless she isn’t fed. But she’s treated like an animal (see documentary, above). The section on how the second generation came to be is unexpectedly nasty.
I had never seen The Exorcist III all the way through. Glad I did, though the story of the Exorcist sequels is a sad commentary on studio idiocy. This movie originally didn’t even have an exorcism and probably would have been better for it. I’m still trying to sort out how exactly this film is connected to the first. Zero connection to the second. But it has George C. Scott and Ed Flanders whose on-screen chemistry is awesome. Plus, as in The Changeling, Scott always seems like he’s on the verge of just being a complete asshole. Which, I suppose, is George C. Scott. Works here. Bonus: this movie contains what was voted somewhere the best jump scare in horror. I don’t disagree; it’s all about the setup. Will let you find it for yourselves.
Back to documentaries, Scream, Queen! My Nightmare on Elm Street is the story of Mark Patton, lead from the second Nightmare, Freddy’s Revenge. The back story on any horror as iconic as this series is great, but this documentary is basically one man’s reply to his portrayal in another documentary, Never Sleep Again: The Elm Street Legacy, itself wonderful. The problem? The screenwriter swears that the script was not intended to be homerotic or to create the first ever male scream queen. The lead, Patton, was a closeted gay man who simply played the part and ended up creating what many consider the gayest horror film ever. (The director seems like a dolt oblivious to any of this.) This was right as the AIDS crisis was shattering America and Hollywood padlocked closets closed. It seems to have ruined Patton’s career. He’s still pissed about it and ultimately confronts the screenwriter.
I’m pretty schooled in the weird Italian sub-genre of cannibal horror. I’ve seen Cannibal Ferox and Eaten Alive and I was the only person in the theater for the premiere of Eli Roth’s love letter to the genre The Green Inferno. But somehow I had never seen the granddaddy, Cannibal Holocaust. I vividly remember the bloody impalement cover of this VHS rental. Every Friday night we’d venture to the video store I’d pass it wondering how they pulled it off. (Turns out, that was a real actress. I mean, wow.) This is a very good film, way ahead of its time. Story within a story, found footage, stomach-churning gore. Yes it has real killings of animals — one is too many, but there are lots — and yes it is horrific in every way. But it’s better than anything that came after it, including Roth’s.
Not a film, but if anyone is into horror comics (showing my age here, but I loved Tales from the Crypt), there’s a new one called Rogue Planet. Space horror, naturally, but pretty fresh. Example: the journey to the rogue planet has crew in hibernation (normal), but a subset of them are periodically awakened by the ship’s AI and used as unconscious, zombie-like drones to do work on the ship before they are returned to sleep and another set of crew are awakened to be human space Roombas. Art is 💯.
Mayhem is a fun movie. Office Space as berserker rage horror-comedy. Steven Yeun, who you may have last seen getting his brains (and eyeball) bashed out on The Walking Dead, is a great pissed-off middle-management lead. Pay attention to the scene by the cubicles. That guy and girl humping like dogs are actually having sex. Why? Because they are local extras and this was filmed in Belgrade. Serbia, man. /shakes head
Re-Animator is one of my favorite horror movies of all time. Probably watch it once a year. But it had been a long time since I watched its immediate sequel, Bride of Re-Animator. Not a bad film at all — quite entertaining, really — but it reminded me that in attempting to capitalize on what came before sequels only ever succeed doing one of two things: 1) go in a completely different direction (e.g. A New Hope → Empire Strikes Back) or copy the first so slavishly that it is essentially the same film (e.g, A New Hope → The Force Awakens). Just don’t get caught in the middle, a celluloid Uncanny Valley kinda, which is precisely where Bride lives. I would have been happy with only reanimated human corpses. No need for weird animal appendage beasties. (And yet, the re-animated head of Dr. Carl Hill with grafted bat wings: A+ for ridiculousness.) Also, some great lines: “TISSUE REJECTION!” and “West, you stupid biped!”
Earlier I mentioned I Spit On Your Grave, but I didn’t realize that a direct sequel called I Spit On Your Grave: Deja Vu — from the original director with the original actress — had been released last year. It tells the story of a woman horribly violated long ago whose vigilantism has made her a minor celebrity in a culture of male perversion that seems not to have evolved one iota in 40 years. In the first film all the blame sits squarely on the redneck rapists. Here it is that but also a much broader swath of society, directly or complicity. This film’s violence can’t possibly be as difficult to watch as the extended rape scenes were to audiences in 1978, but it should be. And maybe that’s the point. #MeToo shouldn’t cause deja vu.
If you like anthology horror with nested narrative frames and lots of 80s video rental store nostalgia then Scare Package is for you. It’s a bit all over the place with wildly different story quality but good for snack-sized, disjointed viewing. I may have thought that Scream, Shaun of the Dead, and What We Do In The Shadows had exhausted the sub-genre of making fun of horror tropes, but I thought wrong. The segment that’s an obvious gooey homage to Troma is my favorite, but the final story’s machete-wielding killer and victim on treadmills as objects of scientific study is pretty hilarious.
I highly recommend Ready or Not. Funny horror but not a comedy, a gothic mystery but the murder hasn’t happened yet. Great performances, lovely gore, and wow is aging Andie McDowell creepy. This should be required viewing the night before anyone gets married.
The Dead Center is a film I heard about on the year-end wrap-up for the Horror Movie Podcast. It’s well-acted and fairly scary, but what I liked most was the premise. Mangled up dude comes into the ER, dies, and is zipped up off to the morgue. Wakes up, finds a gown and an open hospital bed, and then the movie happens. He’s not right, of course. Worth a watch.
I love Octavia Spencer and she didn’t let me down in Ma. Apparently she wasn’t the first choice for lead in this film, but man was she creepy. The flashback backstory is just enough to flesh out her character. And I could totally see myself falling into her trap like the teens in this movie do. Total recommend.
Sweetheart and Sorority Row: Any movies where the first death is by coral or which involve Carrie Fisher with a shotgun (Blues Brothers!) start off with an A on my grading scale.
The Beach House is a bleak, beautiful winner. Small cast, well-acted, eerie if not terrifying. The visual aesthetic may be the first time I think I see Ari Aster’s vibe in another director’s work. Also reminded me of some of Eli Roth’s non-Hostel films where the first half might as well be a good, normal-ish drama — and then it all falls to hell. Marine biochemist as final girl? Sign me up.
Turns out I had seen The Guest before, but I did not realize it until the very last (unsettling) shot. Must be good if that’s what stuck with me. It’s really about the family trauma of the Iraq/Afganistan wars — a thriller with a definite horror vibe, especially the final set-piece. If you’re suspicious of houseguests in general, you’ll probably like this.
Would you believe I had never seen Halloween III? I remember loving the VHS cover art, but that it was critically panned mostly because it had nothing to do with Michael Myers. (But he is in it briefly! Also I swear I heard a slowed-down version of the original Halloween theme, which would make sense since Carpenter scored it.) It’s a really good flick. Tom Atkins (the mean dad from the Creepshow frame story) is excellent and Dan O’Herlihy (the CEO from Robocop, I think) is perfect in his role. Great ending. Still don’t know what “Season of the Witch” means in the title. More like Leprechaun meets the commercial critique that became They Live. I think I would have dug the idea for the Halloween series being a totally different film each entry, but that didn’t happen. It’s what we have Trick R Treat for, if they’d ever make another one.
The Wretched is actually about a witch. In addition to being gross to look at and not at all nice, she also has the power of making people forget things, which is why this is a movie you gotta pay attention to. Truly excellent ending. It’s Smart Horror™. Is this a trend?
Need less high-minded, not even passably well-made horror? Blood Feast 2: All U Can Eat is the movie for you. The original Blood Feast was made over 40 years ago and is interesting for how radical its gore was at the time. Premise: caterer falls under the spell of an Egyptian artifact and goes full cannibal chef. The sequel is exactly the same, but a thousand times worse. And by worse I mean absolutely gratuitous boobs, ridiculous gore, a bizarrely recurring sample from an Orbital tune, and masturbation into a creme brûlée. This is a good film to watch after smoking a lawn bag full of weed, I’d wager.
To those of us with aging parents or grandparents the premise of Relic might cut a little close. It’s about an elderly mom/grandma suffering from dementia. Or is it demonic possession? (These pathologies are not etymologically related; I looked it up. But would have been cool.) It’s disturbing in the same way Hereditary proposes a kind of inherited evil. This film is not to be confused with the so-90’s film The Relic, which was shot at Chicago’s Field Museum, also worth a watch.
In The Darkness the central character is an autistic child with a special way of seeing and relating to something really bad he picked up in the Grand Canyon. It’s a rip-off of Poltergeist mostly but worth mentioning because Kevin Bacon is in it. Setting aside his iconic, pattern-setting death in the original Friday the 13th (just had sex + laying in bed smoking a joint = you about to die horribly) there’s an Ethan Hawke-in-Sinister vibe here. Talented, established actor coming to horror late in his/her career. Paul Reiser is also in this film, for some reason.
As background listening/watching I’ve enjoyed the amateur — but very smart — “Anatomy of a Franchise” series on YouTube. The narrator deconstructs six horror franchises focusing mostly on the evolution of their stories as a series. You’d think the pattern would be a great film (maybe two) followed by dreck, but that isn’t always the case. And even when it is, the narrator explains why. I learned things.
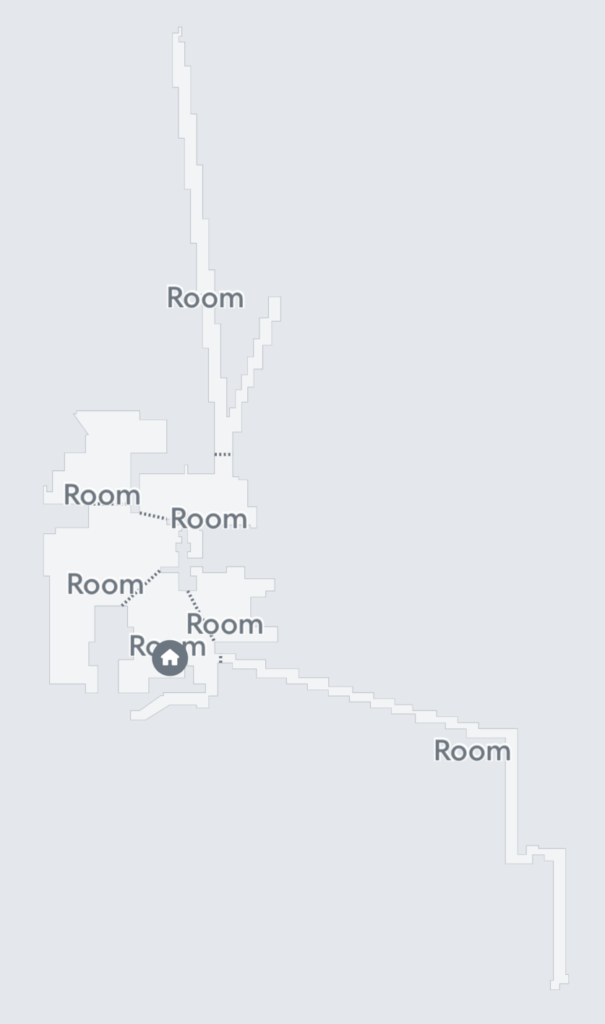
Lastly, if you like experimental horror fiction I was recently reminded of House of Leaves, which I read years ago, by the map my Roomba drew of the second floor of my house. See, the book is about a guy trapped in a house that seemingly never ends, a kind of architectural Tardis which is also a book. The creepiness comes mostly from the non-Euclidean geometry of the rooms (as in, for instance, doors where they physically could not exist — sorta the way Kubrick built The Overlook interiors to make no contiguous sense — watch the documentary Room 237 if you want more on that). Anyhoo, here’s the map that shows the other dimensions the Roomba burrowed into in my house.
Primal Screen is a weird multiple person “memoir” about the creepiness of ventriloquist dolls. It’s a very personal attempt at figuring out what makes dolls so disturbing.
The Siren – A modern retelling of the Greek myth. That it takes place on a lake somehow makes the idea of a seductive sea creature scarier to me. The protagonist is mute, which makes for some very emotive acting. (Probably some deeper meaning I’m not grasping too, since the sailors in the original story made themselves temporarily deaf to thwart the sirens.) Worth a watch, er, listen.
If you’re in the mood for an epically long documentary, have a look at In Search of Darkness: A Journey into Iconic 80’s Horror. It covers basically everything about 80s horror from the franchises to some films I had never heard of, sound design to cover art, nudity to final girl feminism. It’s comprehensive, but there’s basically zero editing. The doc jumps from topic to topic scattershot. Still, I learned stuff. Makes great background watching.
Talk about a movie of/for the moment, Host is what happens when a Zoom videoconference goes to hell. I had low expectations, figuring it would be a knockoff of Unfriended, but it was actually really novel in places. I suppose you have to know Zoom’s quirks to fully get it. There’s one feature of Zoom — and how it could be twisted in the film — that was supposedly the inspiration for the whole thing.
Watched this a while back, but was reminded of it in the doc above. Society is one perverse movie. From 1989, I’m not even sure it could get made today. Suffice to say that this deeply anti-classist flick culminates in one of the nastiest endings I’ve ever seen. It’s called The Shunting and it’s basically what an orgy orchestrated by H.R. Giger would look like.
We Summon The Darkness is an ode to 80’s metalhead culture and the conservative forces who thought we were all satanists. But the real reason I watched it is that I have been a sucker for anything Alexandra Daddario is in since the Texas Chainsaw remake. I’m surprised there have not been more films that play with the Tipper Gore mania around pentagrams and dove-decapitation of that time. This one kinda nails the tone as I recall it.
I mean, a horror movie about a vinyl record that kills you when you listen to it? TAKE MY MONEY. Deadwax is a series of super-short “episodes” totaling less than two hours. (Maybe they were going for tracks-on-a-record thing?) Given that audiophiles and vinyl collectors are somewhat insane to begin with, this is fertile subject matter. I particularly liked the subplot involving Lac beetles, the creepy-crawlies that make natural shellac, a rare early material used to make records.
The Rental falls into a category I am now thinking of as Sharing Economy Horror. Clearly inspired by stories of creepo Airbnb owners, this is the tale of two intertwined couples on a weekend getaway that ends disastrously. Really the protagonists are the horrible people in this film, though there is of course more to it. Incredible sound design.
Cold Prey, because sometimes you just need a bunch of horny young adults trapped by a pickaxe-wielding killer — and nothing more. This film is standard fare in every way, except that it’s Norwegian. (I switched the overdubbing on briefly, ruining the tone of the film completely. Recommend subtitles.)
1BR explores the fine line between homeowner associations and death cults. Sounds funny, but it’s played completely straight, and it works. Final shot is wonderful and frightening.
This one kinda messed me up. Swallow is about pica, the compulsion to eat dangerous things. I’m not sure why reviewers call it horror, except that this is exactly what I felt watching the lead do the swallowing. It’s aesthetically beautiful, deeply unsettling, and superbly edited.
I had high hopes for the horror comedy Extra Ordinary, but maybe it was too British for my taste. Some good moments — homage to The Exorcist poster art, strategy for saving the virgin from sacrifice — but I did not find myself LOL’ing like I did during What We Do In The Shadows.
Color Out Of Space feels like a companion to Mandy at least from a visual saturation and Crazy Nic Cage perspective. I don’t know the original Lovecraft story so I can’t compare, but it had it’s moments for sure, e.g. horribly mangled, still-writhing devil alpacas. I like the idea of an evil that is just a color, but I could not unhear “Colorspace Error” from improperly rendered PDF files.
I had seen Life before but did not realize it until the very last scene (that’s twice now), which is easily the most unsettling. Great acting lineup — though if you are in it for Ryan Reynolds he’s not really the lead. It’s maybe a good reminder about the resilience/persistence of life in these dark times, but in a most horrible way. If you like spaceship corridors and killer aliens, dial this up.
Gretel & Hansel is a gorgeous film. Sophia Lillis of IT fame is wonderful too. Not pee-your-pants scary, but the effects are great and the witch is suitably witchy. Worth a watch if only to ask yourself how on earth Grimm’s tales ever were thought appropriate for children.
Bulbbul is Bollywood horror because of course that exists. This is a beautiful film that absolutely does not follow western horror conventions. More of this, please.
I missed Eden Lake when it came out, but I’m sorta glad I did because I’m not sure I would have understood it in the same way if I saw it in 2008. Basically UK torture porn with some nasty classism as scaffolding. I was troubled by this flick since the overall message, if one was meant, is exactly the bring-back-the-good-old-days of Merry England delusion that powered the Brexit vote 8 years later.
Devil’s Gate was one ambitious take on aliens and crazy rural folk. Enjoyed it as I repeatedly thought I wasn’t enjoying it. Two points of note: 1) I think this is the first time I have seen Jonathan Frakes in anything since Star Trek: TNG. He is also borderline obese. 2) The female lead is quite good, but I did not realize until I looked it up that she is not, in fact, Naomi Watts.
Deep Blue Sea 2 – This is an atrocious movie. Not a remake of the Renny Harlin goofiness (which I loved), but almost the exact same movie. Do not view.
Deep Blue Sea 3 – Also atrocious, with a side of white savior. Thanks Shark Week! Also a do not view.
The Babysitter legit made me laugh and cheer throughout. Its sequel, The Babysitter: Killer Queen, was not quite as funny and did not have the same shock value, but I recommend a watch. The dialogue is rapid and witty. Ken Marino as the dad was hilarious. (Alas Leslie Bibb as the mom was underused. A shame since she was A+ in Hell Baby.)
What a unique film is Belzebuth. This take on the second third coming of the Antichrist is equal parts disturbing, scary, and fresh. Plus, it’s as much a Mexican film as an American one. The dialog just switches back and forth between languages depending what a person would naturally speak. Understated but powerful commentary on border crossings and imperial evil, too.
I loved the horror-thriller The Perfection. Twist after twist after twist. Features Allison Williams from Get Out who I am now convinced is a straight-faced maestra. I’d hate to play her in a game of poker. You can almost feel the specter of Harvey Weinstein in this story (irony: a Miramax film). Best line in a long time: “There are maggots in my puke”. Highly recommend!
I should have known that House of the Witch was a horrible movie, given that it was made for TV. Production values and trope/trick rehashing are laughable. Thesis: Amazon Prime’s cellar-grade films are shittier than Netflix’s stinkers.
Usually it’s a bad idea to watch a movie based on its title alone, but The Cleaning Lady did not disappoint. Simple, tight, and not at all what I was expecting. Note: a sub-plot around child abuse, though the worst of it is not depicted, is stomach-churning. Ending was a bit head-scratching.
Sidenote: I rarely read horror, but I thought I would give The Living Dead by George Romero a shot. It was unfinished at his death so completed by a collaborator. Not as jaunty as Brooks’ World War Z novel (which I loved more than the film that I liked a lot), but I am reminded of how different — and lingering — the narrative description of terror can be from when I tore through the Stephen King catalog as a high schooler. I have not finished the book yet and some reviews note that it’s not what it seems like at first, so …
The Binding (Il legame) – Southern Italian curse. Lots of creepy old Italian women. The plot is basically my extended family. I wanted this to be great. It was not great. Consider it watched so you don’t have to. But happy to scare you with tales of my crazy ancestors.
American Murder: The Family Next Door – Documentary on the Colorado dad who murdered his wife, two daughters, and unborn child. What I found engaging was that it was neither a re-enactment nor just talking head experts. Most of the footage here is primary source: social media family videos and personal videos (the wife, Shanann, recorded herself a lot), police body cam video, and contemporaneous news footage. If you believe in the horror of the mundane, this is it. And sadly true, of course.
The Walking Dead: Season 10 Finale – Not sure how many of you have followed this show through the years, but this season — which I found quite a bit more original than previous — was cut off by the pandemic right before the final episode, an unintentional cliffhanger. Possibly unintentionally climactic too. Might have flowed better without building expectations all these months. But it was still great. And the actual ending has a fantastic cliff scene. No hanging.
The Strangers: Prey at Night – I had seen this flick a while ago, but I must have forgotten about it the moment I watched it. Which, well, there’s your review. Not nearly as simple or creepy as the first one. And yet I do have a soft spot for the home invasion genre, so what if the homes are a trailer park. You really can’t beat the answer in the first film to “Why are you doing this to us?” (“Because you were home”), though this one tries: “Why not?” Completely motiveless murder (not unlike Eden Lake).
The Haunting of Bly Manor – I put some time into this follow-up to The Haunting of Hill House which is still the best horror I have seen in the last few years. Bly Manor is not in any way connected to Hill House except that some cast members return in new roles. But it’s Mike Flanagan so there’s always something lurking out-of-frame. Much deeper, more philosophical, and frankly less scary. But worth the investment of time. It’s a great remix of The Turn of the Screw. Plus setting a show in the 1980’s amidst the poshness of an English country estate is itself weirdly unsettling. Recommend.
Scare Me – Very interesting film. Just two people (then three, then two again) telling each other ghost stories. Like, that’s really all there is. Except that there’s more, ultimately. Creative, funny at times, and super tight. Highly recommend. (If you go looking for this, make sure you grab the film by Josh Ruben. There’s another horror film with the same name released this year.)
The Cleansing Hour – Fair to say there’s an entire horror sub-genre now where fake exorcists (or ghost-hunters) do their exploitative thing until — uh oh! — they stumble upon real evil. This is that. Kind of a good plot too. Very uneven though. It’s like some parts of the film had talented actors and a decent budget and other parts did not. Might have worked better not played straight. I mean, if you’re gonna make your audience chuckle you might as well intend to do it.













